Variables Overview
Learn about Variables in WaveMaker low-code platform. See how it works and how to use them as services.
Variables form the glue between the frontend UI and the backend services. Variables provide data integration for the widgets.
Scope of Variables
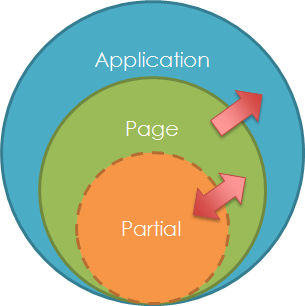
Variables and Actions can be classified into two based on the scope of the Variable. The two types of variables are - Application and Page level variables. While both these types reside at the client side, the application level variables share the data across multiple pages, whereas Page level variables share the data within the page where they have been declared/created. Whenever you are switching from one page to another, all the previous page level variables are destroyed.
It is advised to have unique names for any variable to avoid confusion. Whenever you try to create or rename a variable WaveMaker will throw an error if another variable of the same name exists either within the page or at the app level.
How it works
Variables function by invoking the associated REST APIs on the server-side, invoking the client-side JavaScript events that are associated or bound by configuration, after the response is obtained. Variables play a significant role in binding the UI and the backend services layer together through configuration and events, eliminating the necessity to write a lot of code.
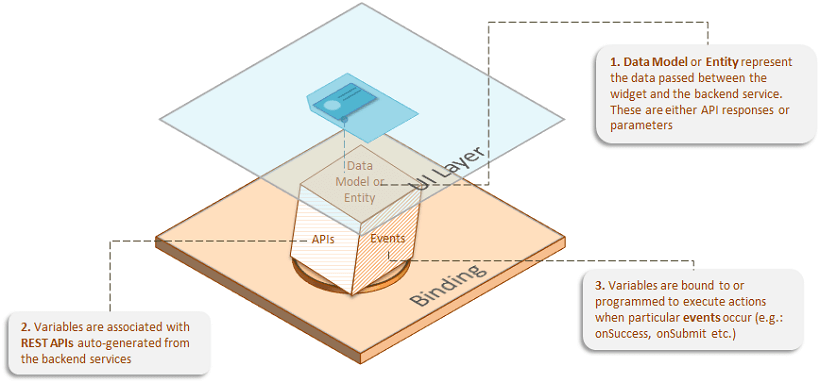
Variables can be represented using a block with 3 faces, as in the picture below, representing the APIs invoked, events processed and the Model or Entity objects returned by the APIs.
Variable Types
Variables can be categorized based on the target action:
| No. | Variable Types | See |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Database CRUD | Database CRUD |
| 2. | APIs | - Database APIs - Web Services - Java Services - Security Services |
| 3. | Other Services | - Model Variable - Device Variable |
1. Database CRUD
The basic insert, read, update and delete operations on an imported database entities can be performed using the default CRUD APIs generated at the time of import by the platform. For more information, see Database CRUD.
2. APIs
Variables can be created to be based upon the various APIs exposed by the services integrated within the app. These can be further classified as as following.
Database APIs
Database import generates several APIs for functionalities like Count, Filter, Get by field name, Get associated table data etc. apart from the default CRUD APIs and can be used for more control over the database. These Database APIs also include those corresponding to Queries and Procedures created within the data model. For more information, see Database APIs.
Web Services
Variable can be created to access the APIs exposed by the imported web service. For more information, see Web Services.
Java Services
For every Java Service created within WaveMaker, its REST API contract is auto-generated and the same can be accessed through a Variable. For more information, see Java Services.
Security Services
In case security is enabled for the app, you have access to various security-related data. For more information, see Security Services.
3. Other Services
Model Variable
To store data on the client side. For more information, see Model Variable.
Device Variable
For Mobile Apps, the various device information can be used to access the respective devices like camera, contacts, and more. For more information, see Device Variable.