Introduction to React Native Studio
Help Us Improve
We're working on enhancing the onboarding experience for WaveMaker developers. If you have feedback on this article, please share it using the Feedback section at the bottom of the page. Your input helps us make improvements that you’d like to see. We're also open to contributions to our documentation. New to contributing? Read more about contributing here Contribute to the help.
WaveMaker Studio for React Native allows developers to build native mobile apps for iOS and Android using web development skills. It simplifies the development process with a visual studio, reusable components, and a fully exportable codebase.
With WaveMaker React Native, You Can
| Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Use Web Skills to Develop Mobile Apps | Develop native mobile applications using familiar web technologies like JavaScript. You can build and deploy apps without needing to learn native iOS or Android programming. |
| Reuse Components with Prefab Architecture | Prefabs are reusable UI and logic components. Once created and connected to backend APIs, they can be reused across multiple apps — promoting consistency and reducing redundancy. |
| Work with an Open and Customizable Architecture | Export clean, standards-compliant React Native code. Integrate third-party React Native libraries and Expo plugins, Avoid vendor lock-in with fully portable projects |
| Development and Testing Tools | - Automated Testing: WaveMaker supports automated UI testing through Appium. - Debugging: Use Flipper for real-time debugging of layout, logs, performance, and plugins. - App Deployment: WaveMaker exports a React Native project zip that can be processed by AppChef to generate APKs (Android) or IPAs (iOS) for distribution. |
React Native App Architecture
Your WaveMaker app is built on top of the React Native framework, combining visual development with native performance. The architecture spans from visual components defined in the Studio to the underlying native modules that run on iOS and Android. The diagram below shows how each layer contributes to delivering a native mobile experience.
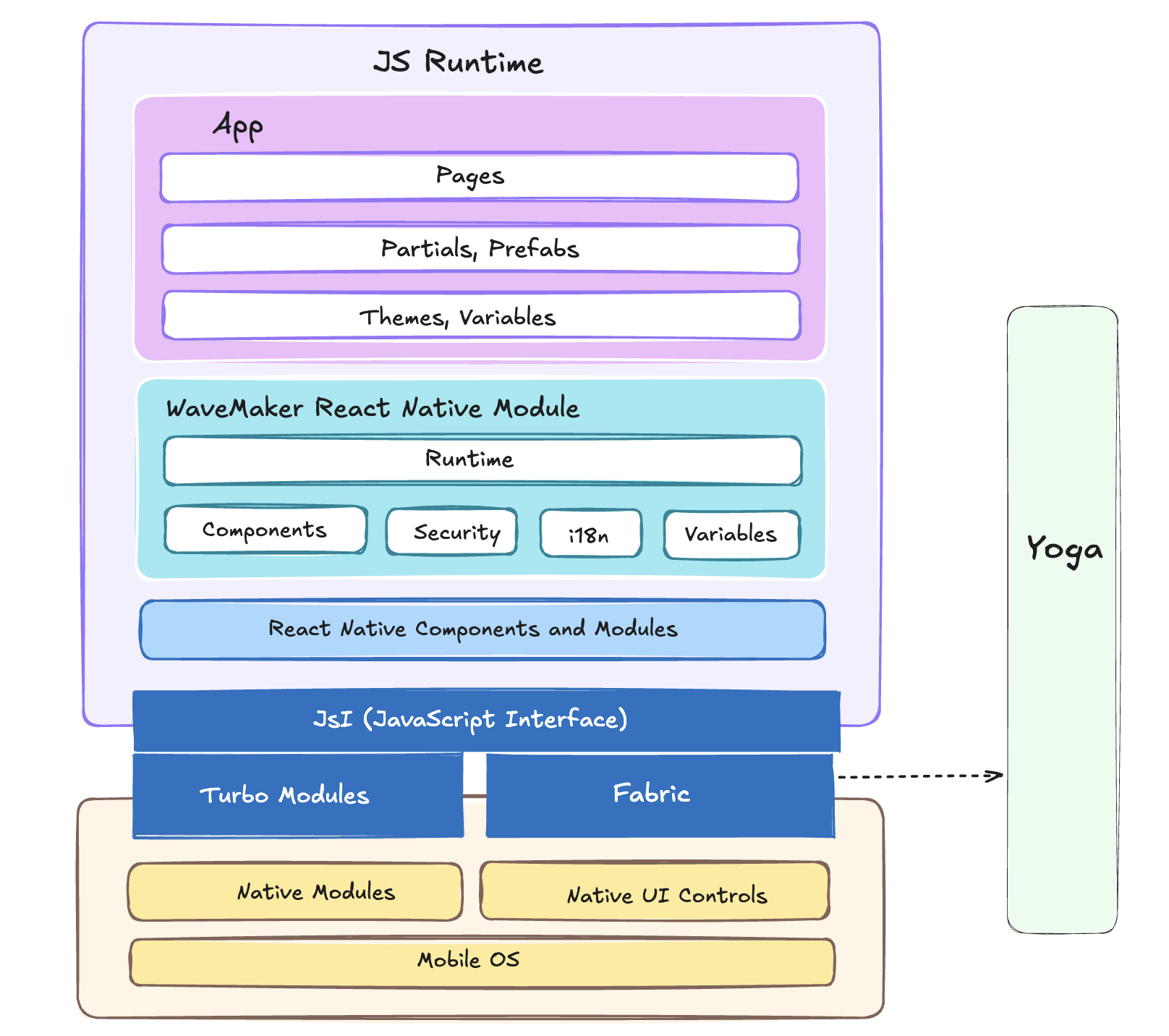
This layered architecture ensures your app logic, UI, and data flow are handled efficiently—from the visual design in Studio to native rendering on devices. With WaveMaker handling much of the complexity, you can focus on building functionality without needing deep knowledge of native code.
Architecture Layers
JS Runtime: The JavaScript engine that executes app logic, manages UI rendering, and handles events.
App: Your visual app built in WaveMaker Studio. It includes:
- Pages: Screens of your app.
- Partials, Prefabs: Reusable UI blocks and widgets.
- Themes, Variables: Style settings and data bindings.
WaveMaker React Native Module: Provides the core framework and runtime for WaveMaker apps, including:
- Runtime: Orchestrates rendering and behavior based on configurations.
- Components: UI elements exposed via Studio.
- Security: Built-in user auth and access control.
- i18n: Internationalization support.
- Variables: App state and data sources.
React Native Components and Modules: Bridges the JavaScript-defined UI to native elements using React Native.
JSI (JavaScript Interface): A bridge layer that connects JavaScript with native code, enabling communication between them.
- Turbo Modules: Optimized native modules accessed via JSI for better performance.
- Fabric: Modern rendering system in React Native for faster UI updates and concurrency.
Native Modules: Platform-specific features (e.g., camera, storage) exposed to the JS layer.
Native UI Controls: Core iOS/Android UI elements rendered by React Native.
Mobile OS: The base layer (iOS or Android) the app runs on.
Yoga: Layout engine used by React Native to calculate responsive layouts across devices.
Build Pipeline
A streamlined build pipeline to convert your app from visual development to an installable native app.
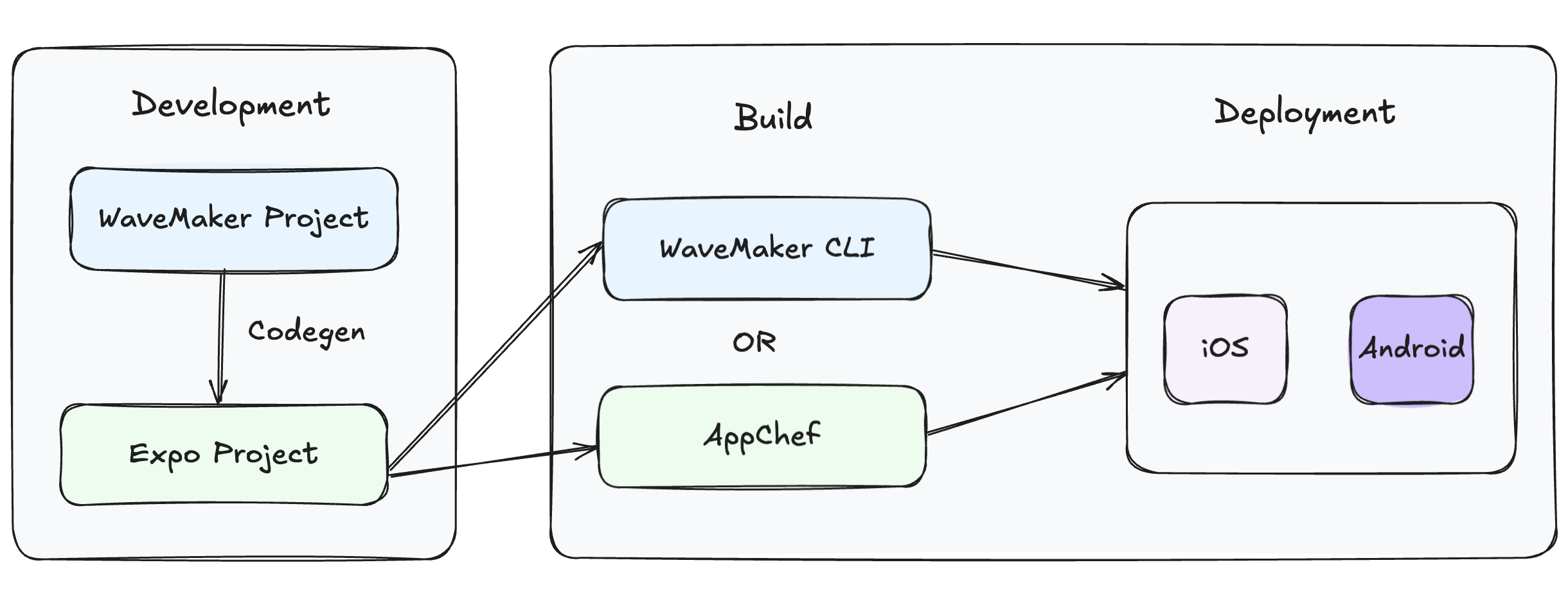
Development
- WaveMaker Project: Design your app visually in WaveMaker Studio using a low-code approach — the platform takes care of the underlying native implementation for you.
- Code Generation: WaveMaker generates a standard Expo-based React Native project. It does not rely on a proprietary runtime, so the output is fully compatible with the broader React Native ecosystem.
- Expo Project: The generated app runs in the Expo environment, making it easy to preview, test, and extend using standard React Native tools.
Build and Deployment
- Build for Stores: Use the WaveMaker CLI or AppChef to convert the Expo project into installable
.ipa(iOS) or.apk(Android) files.
In WaveMaker React Native Studio
Markup and Variables
WaveMaker uses Markup to define the UI, Variables to integrate backend services, and JavaScript for logic. React Native has its own rules when it comes to styling, scripting, and data integration, so it’s important to understand the differences.
- Markup: WaveMaker markup is converted to React Native markup during build.
- Variables: Variables act as a bridge between the frontend UI and backend services, integrating data and services with the widgets. Learn more about the supporting React Native Variables here.
Things to Note
React Native has a unique way of handling styling, scripting, and data integration, which differs from traditional web development. Understanding these distinctions will ensure your WaveMaker React Native app functions smoothly on both iOS and Android.
In WaveMaker, apps are developed with WaveMaker Markup, Variables, JavaScript, and Styles defined in CSS. However, React Native development has specific rules:
- Script: All UI and Variable event callbacks work as expected, but web browser APIs are not supported. HTML DOM amending JS libraries (e.g., jQuery) do not work on mobile apps. Adding external JavaScript via HTML
<script>tags is not supported. Use npm packages to include third-party libraries.
Let me know if you need a similar note for native libraries or styling assets.
Styles: In WaveMaker, styles are typically defined in CSS, but React Native does not support CSS. Instead, React Native styles must be defined using JavaScript. WaveMaker allows partial CSS usage for development. For more information, refer to the React Native Style API Documentation. Be sure not to add CSS classes copied from the web preview HTML DOM tree.
Themes: React Native supports Themes. Learn more about how to generate themes.
Prefabs
Prefabs are reusable components that can save time and effort, especially for larger projects where components need to be shared across multiple platforms. A Prefab can be used in a web app, or a React Native-based mobile app. To ensure that a Prefab renders properly across platforms, follow these guidelines:
- The stylesheet of a prefab should be divided into two parts by the line. After the line above, you can place styles specific to the React Native environment.
- Adding a JavaScript file is not supported.
- Widgets that are not supported by the WaveMaker React Native runtime will be discarded.
By following these guidelines, you can create Prefabs that are compatible with React Native, and web platforms, ensuring maximum reusability and consistency.
Note on Custom Formatter
You can use the Custom Formatter to adjust the data before displaying it on the mobile app, ensuring better user experience and performance. React Native has started supporting customization of data using Custom Formatter from Release 11.3. For more information, refer to Custom Formatter.