ORM Artifacts
Integration of WaveMaker app with database generates few files, services, and APIs. These are used internally by WaveMaker to achieve the seamless integration. This information is for advanced developers who want more control or need more information for academic interests.
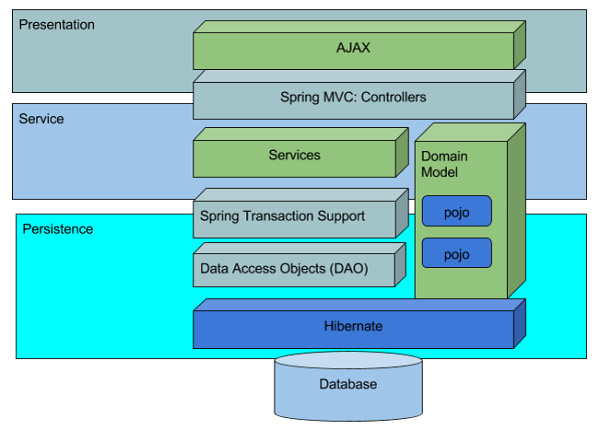
Layered Architecture
When a database is integrated into a WaveMaker app, it generates the source code for CRUD operations for each entity within the database. In addition to the CRUD APIs, the filter, count, and export APIs are also generated. Associated APIs in the case of related tables are also generated.
The source code is generated with the ORM, Service Layer & REST APIs with each layer having a specific responsibility:
- Layer 1: REST Controller is responsible for transporting the data between client and server, authorization of APIs & marshaling and unmarshaling of the model to JSON etc.
- Layer 2: Service Layer is responsible for validating the inputs and transaction management
- Layer 3: DAO Layer is responsible for interacting with the underlying database
The following diagram depicts the Layered Architecture mentioned above:
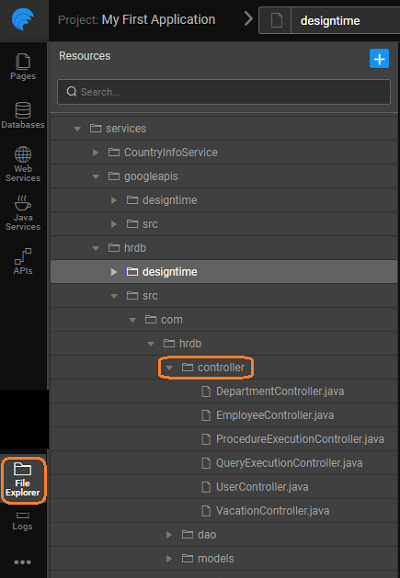
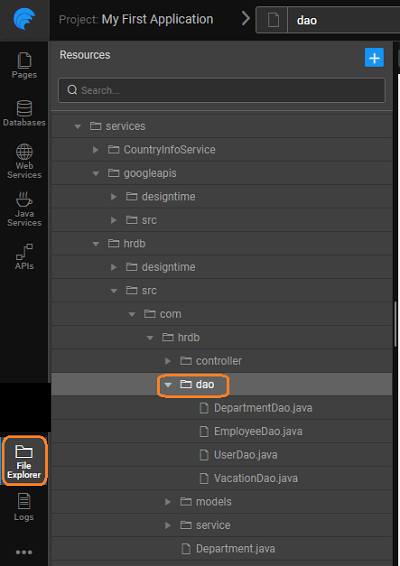
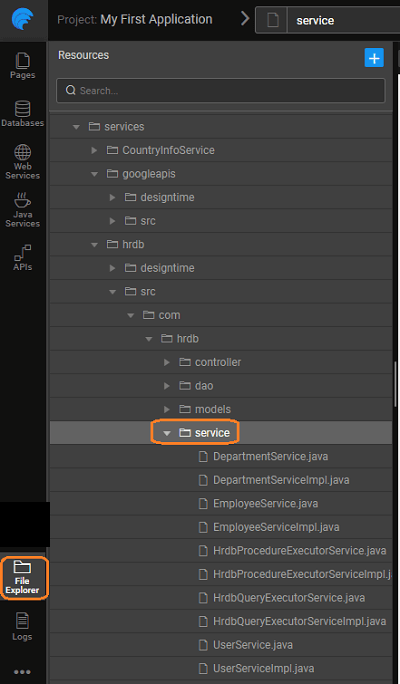
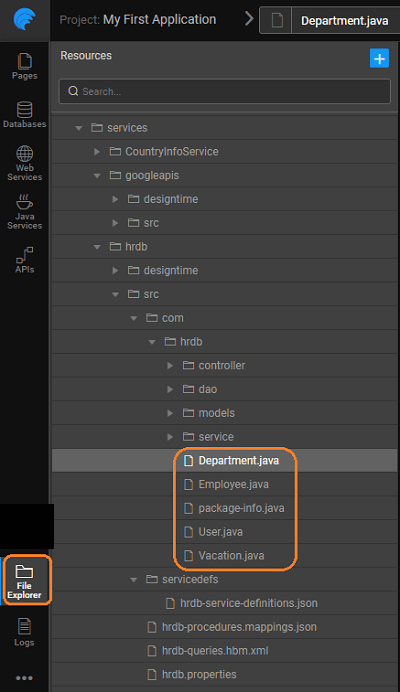
Generated Files
The folder structure for the generated code is as follows:
- Controllers generated for entities (one for each entity), queries and procedures:
- Data Access Objects (DAO) for each of the entities:
- Service Interfaces and Service Implementations for entities, queries, and procedures
- POJOs for each entity
Each of the layers performs its function and delegates the call to the next layer in the chain. For example, after the unmarshaling of the JSON data to the model, and authorization checks, the REST layer delegates the call to the service layer, and more.
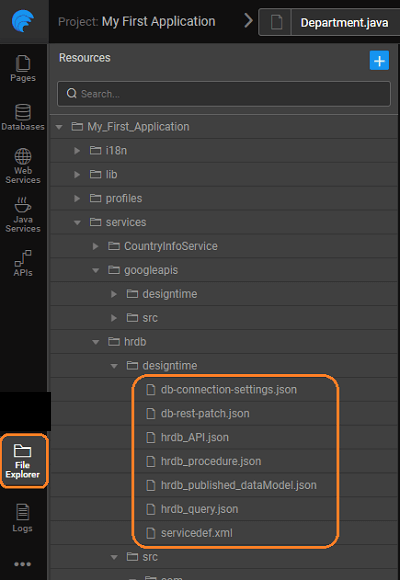
Design time Configuration Files
It contains files required for designing database.
db-connection-settings.json: it contains connection properties.servicename_API.json: Generated API specification (swagger) of given service.servicename_procedure.json: contains information regarding procedures for that service.servicename_query.json: contains information regarding query for that service.servicename_published_datamodel.json: contains database schema information. It plays a major role while updating DB changes. Whenever you do manual changes in the database you have to re-import to update this file.servicename_draft_datamodel.json: Contains user modifications. It’ll delete when we do update/re-import database.servicedef.xml: contains types information for this service.
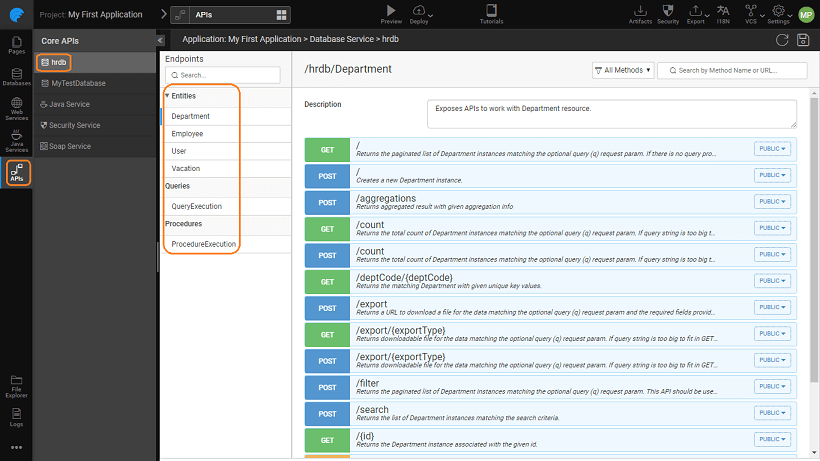
Generated APIs for Database Services
Import or creation of database within a WaveMaker app results in the auto-generation of ORM artifacts from the Database Schema and as such each Schema needs to have a Primary key either single or composite.
In case your external database schema comes without a primary key, you need to assign a column(s) as virtual primary key else all the columns are treated as part of a composite primary key. For each entity imported, a REST API is generated for each of the CRUD operations, Filter and Count functionalities. These REST APIs are exposed via the API Designer and can be tested and reconfigured as per the application needs.
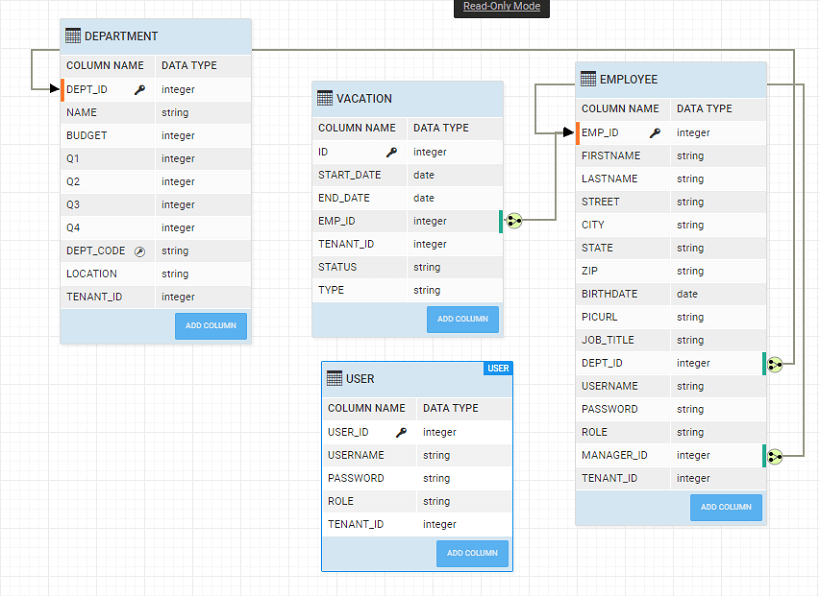
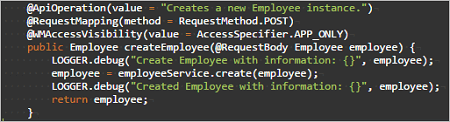
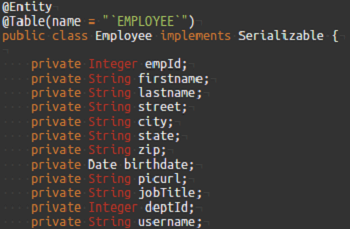
As an example, we are using the following Employee-Department Database Schema (Sample hrdb that can be imported into Studio) with a unique constraint for Dept_code on the department table:
Request Mapping:
Example:
CRUD APIs
Create
Inserts a record into the table.
- URL: /
- Request Type:
POST - Path Variables:
None - Request Parameter:
None - Request Body:
object in JSON format - Method Name Example:
createEmployee
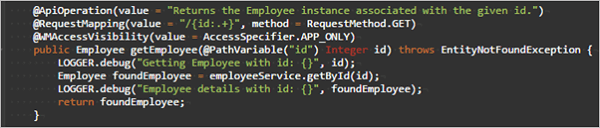
Read (primary key based)
Retrieves the data associated with given ID value.
- URL:
/{id} - Request Type:
GET - Path Variables:
primary key column value - Request Parameter:
None - Request Body:
none - Method Name Example:
getEmployee
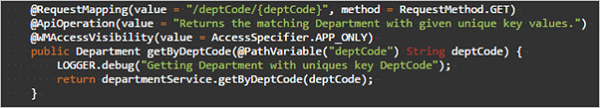
Read (unique key based)
Retrieves the data associated with given unique key value.
- URL:
/[UNIQUE_KEY]/{unique_key_value} - Request Type:
GET - Path Variables:
unique key column value - Request Parameter:
None - Request Body:
none - Method Name Example:
getByDeptCode(unique key for department entity)
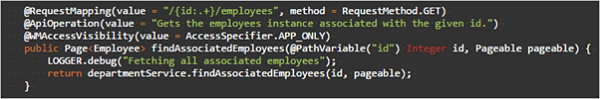
Read (foreign key based)
Retrieves the data associated with given ID value from the related table.
- URL:
/{id..+}/[relation_field] - Request Type:
GET - Path Variables:
primary key column value - Request Parameter:
- Page,
- Size,
- Sort
- Request Body:
none - Method Name:
findAssociatedEmployees(employee foreign key for department entity)
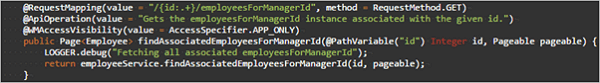
READ (foreign key based - self-referential)
Retrieves the data associated with given ID value
- URL:
/{id..+}/[relation_field] - Request Type:
GET - Path Variables:
primary key column value - Request Parameter:
- Page,
- Size,
- Sort
- Request Body:
none - Method Name:
findAssociatedEmployeesForManagerId(foreign key)
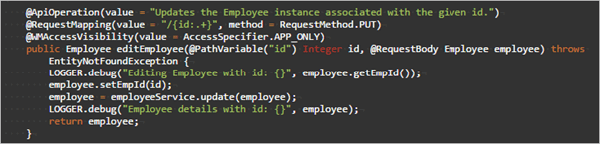
Update
Updates entity record associated with the given id value
- URL:
/{id} - Request Type:
PUT - Request Type:
primary key column value - Request Parameter:
None - Request Body:
object in JSON format - Method Name Example:
editEmployee
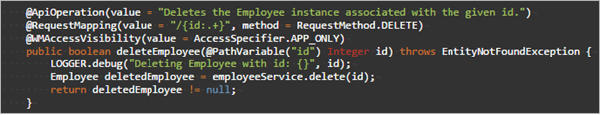
Delete
Deletes entity record associated with the given id.
- URL:
/{id} - Request Type:
DELETE - Request Type:
primary key column value - Request Parameter:
None - Request Body:
None - Method Name Example:
deleteEmployee
Query APIs
Though the following APIs are available in POST and GET type, GET APIs might fail if the request URL is longer than 2048. It is advisable to use POST request type.
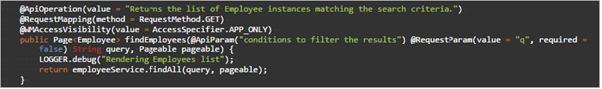
FILTER
Returns the list of entity instances matching the filter criteria (all values if query is not given).
- URL:
filter - Request Type:
POST/GET - Request Type:
None - Request Parameter:
- custom query (optional, see here for query syntax),
- Page,
- Size,
- Sort
- Request Body:
NoneMethod Name:findEmployees
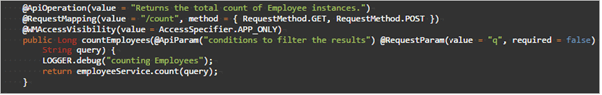
COUNT
Returns the count of filtered entity instances (total count if query not given)
- URL:
/count - Request Type:
POST/GET - Request Type:
None - Request Parameter:
custom query(optional, see here for query syntax) - Request Body:
None - Method Name:
countEmployees
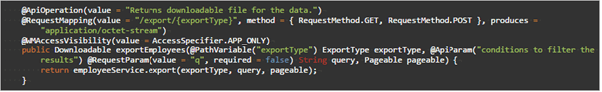
EXPORT
Returns the downloadable file url for the filtered data
- URL:
/export - Request Type:
POST - Request Parameter: pageable - pagination and sorting options, see here for more,
- Size,
- Sort
- Request Body: ExportOptions (Body)
- custom query (optional, see here for query syntax),
- fields list (optional):
- exportType - data format for export can be EXCEL or CSV
- fileName: exported file name
- Method Name Example:
exportEmployees
Custom Query Syntax
The APIs generated by WaveMaker for all the imported tables will have methods that take a query as input. Here we will look at the usage of such query in APIs.
APIs that use HQL Queries: The Filter, Count and Export API in every Table Controller will use the HQL query, which is an optional parameter, for retrieving the data. These APIs can be found in respective tables’ controller class file.
Filter API
This API returns the list of Entity objects that matches the given filter conditions in the query. If query param is empty, API returns all the Entity objects.
Count API
Returns the count of Entities that matches the given filter conditions in the query. For an empty query, it returns the count of all Entity objects.
Export API
Returns a downloadable file with the list of Entities that matches the given filter conditions in the query. For an empty query, we get all the Entity objects.
Query Composition
The HQL query mainly consists of four types of parameters.
- Field Name
- Value Expression
- Value
- Logical Expression
Aggregate functions (avg(), sum(), min(), max()) in HQL query are currently not supported with these APIs.
FieldName parameter
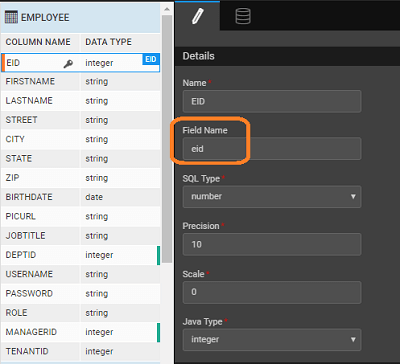
- The fieldName refers to the name of the field associated with the column in the respective table. The field name is derived from the column name in the table and usually camelCased.
- The name of the field for a given column can be seen from DB Designer or the respectively generated model class. Field Name of a column can be found in DB designer on the selection of respective column in the properties panel.
- Relational field names - In order to filter values with respect to an entity in relation, fieldname must be given as entityfield.fieldname. This is applicable only for ManyToOne and OneToOne Relations. Eg:
department.name = ‘Engineering’, the name is the fieldname ofDepartment.java
Value Expression parameter
Supported value expression types are listed in below table
| Operation | Expression | Supported Value Types | Result | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| equals | = | Number or String | Values that equals to given value | - empId=1 - firstname=’Eric’ |
| not equals | != (or) < > | Number or String | Values that are not equal to given value | - zip!=02127 - jobTitle< >‘Engineer’ |
| between | between | Date or Number | Values between given range | - birthdate between '1973-10-21' and '1986-06-18' (using date format - YYYY-MM-DD) - zip between 14231 and 15922 |
| less than | < | Number | Values less than given value | - empId<6 |
| greater than | > | Number | Values greater than given value | - deptId>10 |
| less than or equal to | <= | Number | Values less or equal to given value | - empId<=4 |
| greater than or equal to | >= | Number | Values greater than or equal to given value | - zip>=11 |
| pattern matching | like | String | Values matching the given pattern | - street like ‘4%Houston%’ |
| starts with | like | String | Values starting with the given string | - firstname like ‘E%’ |
| ends with | like | String | Values ending with the given string | - lastname like ‘%e’ |
| containing | like | String | Values containing the given string | - lastname like ‘%e%’ |
| in | in | Number or Date or String | Values in the given set | - zip in (‘14231’, ‘02127’, ‘11212’) - birthdate in ('1973-10-21' ,'1986-06-18') - firstname in ( 'Sally' , 'William' , ‘Amanda’ ) |
| null | is null | String | Values satisfying given condition | - role is null |
| not null | is not null | String | Values satisfying given condition | - date is not null |
| empty | = | String | Values satisfying given condition | - lastname = ‘’ |
| not empty | != (or) <> | String | Values satisfying given condition | - lastname <> ‘’ - lastname != ‘’ |
Value parameter
The “Value” parameter is the comparison value for the given field name. The value should be single quoted for non-numeric types. The format for the value of type date is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’.
Logical Expressions
- A logical expression in HQL does one of the following:
- joins two or more conditions to form a complex query
- alters the logic of the conditions
- Supported logical expressions with examples are listed below
- Order of execution of conditions can be controlled using parenthesis. Eg: (empId=4 AND zip=02127 ) OR (city like 'New York%' OR birthdate between '1991-01-01' and '1999-12-31' )
| Logical Expression | Results | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| AND/and | Result set satisfying both conditions | empId>5 AND firstname like ‘A%’ |
| OR/or | Result set satisfying either of the conditions | empId=5 OR deptId=1 |
| NOT/not | Result set satisfying negation of the conditions | NOT ( firstname like ‘A%’ AND empId=4) |
For further reference to HQL query http://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/orm/4.3/manual/en-US/html/ch16.html