Java Service
Overview
Java Services allow app developers to write custom business logic or enable integration with 3rd party libraries and tools and are deployed on the Server side. For every Java Service created in WaveMaker, its REST API contract is auto-generated and is ready for integration with front-end layer (web or mobile).
Variables are required to invoke Java Service methods, each Variable can be configured to take the necessary method parameters required as data inputs and return JSON response. Variables internally perform the necessary conversion to invoke the equivalent REST API endpoint/resource for the Java Service methods.
Creating a Java Service
When you create a Java Service in WaveMaker, Java sample file is created. You can access this file from the Java Services Resources. You can edit the file and even delete the service.
A Java method can have input and output in the form of an individual or a set of parameters. These parameters can be of the following types:
Input parameters
Input parameters can be of the type:
- primitive objects,
- POJO classes,
- a collection of POJO classes and primitives,
- page
- Http servlet response/request which can be passed as URL-based header params or in the form of cookies
- a pageable object with values pertaining to the page to be retrieved, the size of each page and sort field name
Output parameters
Output parameters can be of the type:
- primitive objects,
- POJO classes,
- a collection of POJO classes and primitives,
- page
Java Services framework
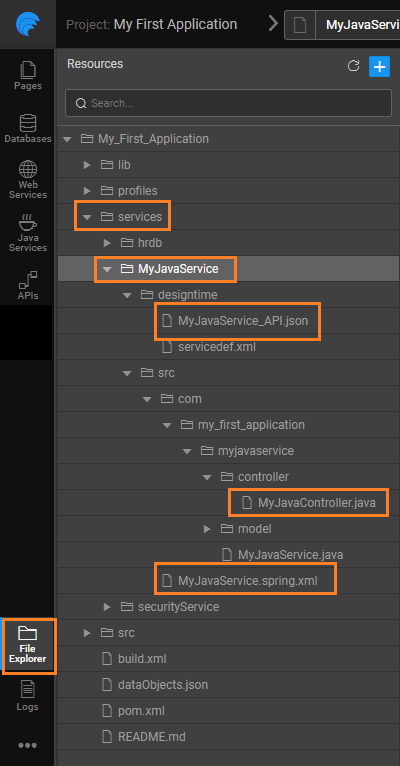
Creating a Java Service generates multiple files, of which the following are of importance:
Spring Controller File
MyJavaController.java, in this example - This file contains the details related to the Java Service. Public methods in the controller class are wrappers of the underlying Java Service code, acting as an endpoint which can be invoked as REST API. The methods can be hidden or exposed to the client using the directives: @HideFromClient and @ExposeToClient, respectively. Request JSON object from the invoking client is automatically converted to POJOs in the method parameter for POST/PUT/DELETE. Similarly, the response POJOs get converted to JSON object.
API JSON File
MyJavaService_API.json, in this example - contains the file structure and details as used by the API Documentation. This is available only during the design time.
Spring Bean Configuration File
MyJavaService.spring.xml, in this example - Bean classes for service/method lookup