WaveMaker product team is able to make weekly patch releases and, feature packed releases every alternate months. Typically product releases involve testing of several micro services, API’s and User interface, functionality etc. WaveMaker platform is composed of several such services, and functional testing can be only done by building apps using visual drag-n-drop studio. To ensure the best product quality for releases, our QA process involves building automation tests for APIs as well as UI functionality using Selenium.
- UI Tests based on Selenium
- API Tests based on RestTemplate
We have multiple environments i.e., Development, Staging and Production for WMO and several on-premise WME environment setups for enterprise customer releases. Our development team uses feature branches and when they merge these branches onto the master branch, we have to make sure all the existing automation tests pass. On a regular basis when each feature team performs a merge, we run a full set of automation tests at their beck and call.
If a new build is promoted to Production from Stage, and at the same time if a merge is performed onto master or a build request is raised to trigger tests in the development environment, multiple test automation setups are needed simultaneously. Imagine, the amount of Devops automation needed to provision, de-provision the infrastructure needed for these test setups and delays caused in the process.
Previously, we used to have a handful of server machines where automation tests for one product environment can be run as a Job on a single machine. To complete the tests it takes a definite amount of time and to parallelize, multiple threads can be configured with each thread running a browser with UI functional tests using Selenium. If the threads are increased, browsers crash due to lack of sufficient memory needed for running selenium tests.
Due to this, We wanted to build a scalable architecture which efficiently utilizes the infrastructure capacity and doesn’t require a lot of Devops effort to scale up and down our automation test setups.
Solution
We explored Kubernetes (k8s) Jobs for test execution and wanted to completely automate the process of automation test setups, No beck and call!
First let us familiarize a few terms used in the Kubernetes world.
Cluster: A cluster is a set of nodes or machines for running containerized applications.
Node: A Node is a worker machine in Kubernetes and may be either a virtual or a physical machine, depending on the cluster. Each Node is managed by the Master.
Pod: A Kubernetes pod is a group of containers that are deployed together on the same host. Pods can be horizontally scale, which represent services in the micro services world.
Job: The main function of a job is to create one or more pods and track the success of pods.
Namespace: Namespaces help pod-to-pod communication using the same namespace. Typically used for application or environment grouping.
Test environment provisioning with k8s
Provisioning separate test setups for different product environments is done by creating separate namespaces for API and UI Tests in a k8s cluster for each environment. For every request to run test automation, a Jenkins task is started that generates a k8s spec file and launches a k8s job.
As the test repo keeps updated frequently by the QA team with new automation tests, we compile and create an image and push it to the kubernetes registry.
Once k8s Job has started, a Pod will be created to execute commands in the k8s spec file given below
- Maven command to execute tests
- Upload test results to s3.
On completion of above commands, respective Job status will be changed to complete.
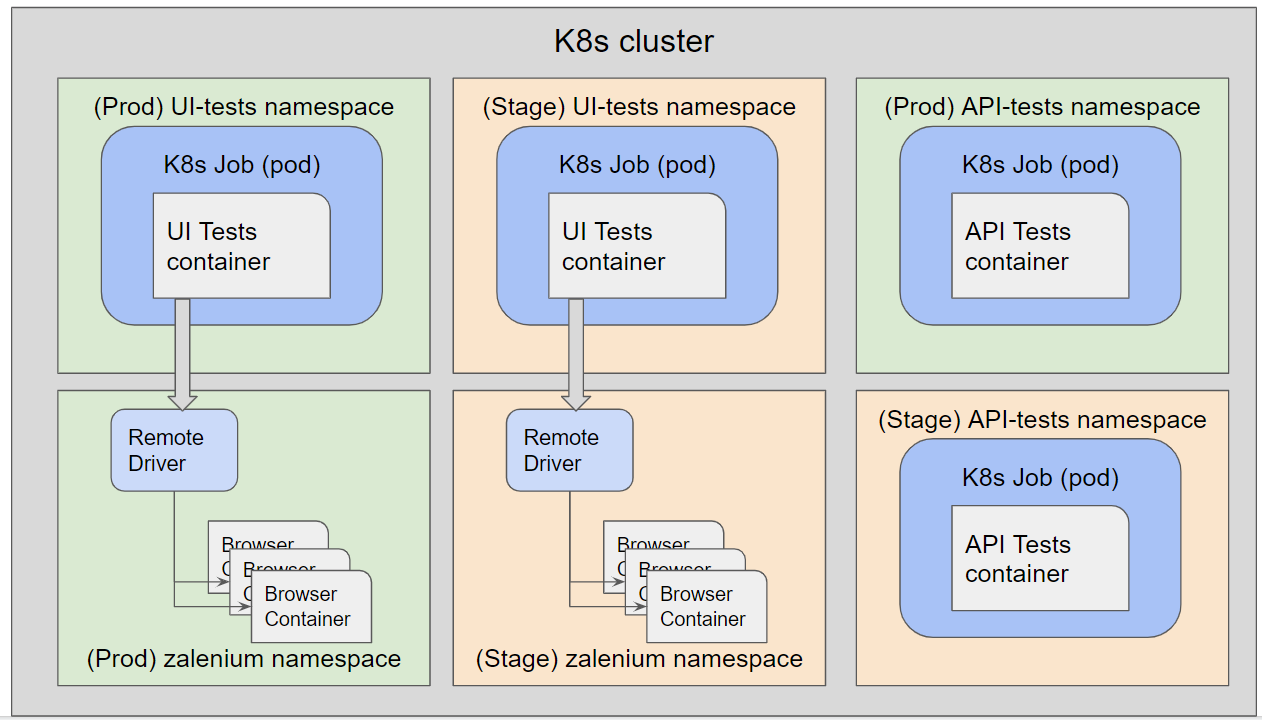
Automation tests for multiple product environments i.e stage or prod, will be executed in a k8s cluster as shown in the below picture.
For each product environment, there will be an API namespace where a k8s job is run to execute all the API tests. For running UI tests, Zalenium is used which requires a separate k8s namespace for running the remote driver and the browser container. K8s job for UI tests communicates to Zalenium’s remote driver and based on the configured threads the browser containers are scaled up to run these UI tests simultaneously.
In the case of test execution for multiple product environments, If resource/memory is not sufficient to create a browser container then k8s cluster can be configured to scale up on demand. After the pod execution is done k8s will perform a health check and close the nodes if no resources are being utilized.
Conclusion
With this approach, our automation test setup provisioning for multiple product environments has been completely automated, we can scale up and down nodes to speed up test execution times due to scalable infrastructure. Since, we have enabled parallel execution of selenium tests using multiple browser instances, we have achieved significant time reduction for running the tests.
| Job | K8s Setup Execution Time reduction |
|---|---|
| Sanity Tests Execution | 55% |
| Regression Tests Execution | 60% (10 hours -> 4 hours) |
| Sanity and Regression as parallel Jobs | 60% |
Checkout what is in our latest release WaveMaker 10.5 here.