WaveMaker supports Redshift architecture to develop WaveMaker apps by importing the Redshift database into the Studio. You can customize tables and perform queries like any other databases supported by WaveMaker to present data in the UI.
How Redshift Architecture Works
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud. You can start with just a few hundred gigabytes of data and scale to a petabyte or more.
Amazon Redshift achieves efficient storage and optimum query performance through a combination of massively parallel processing, columnar data storage, and very efficient, targeted data compression encoding schemes.
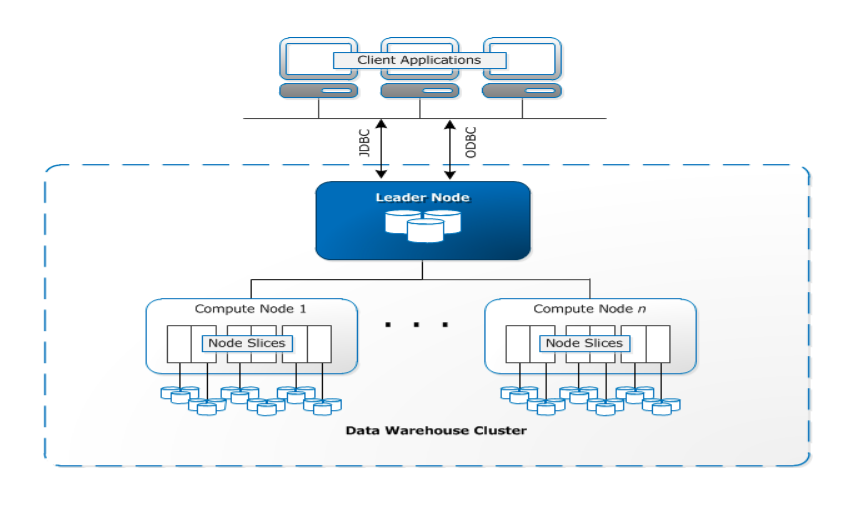
Redshift is a data warehouse cluster which is a combination of nodes. If a cluster has two or more clusters then an additional leader node exists which coordinates between the nodes and handles external communication. Each compute node has its own dedicated CPU, memory, and attached disk storage, which are determined by the node type.
A compute node is partitioned into slices. Each slice is allocated a portion of the node's memory and disk space, where it processes a portion of the workload assigned to the node. The leader node manages distributing data to the slices and apportions the workload for any queries or other database operations to the slices. The slices then work in parallel to complete the operation.
Redshift in WaveMaker
From version 10.7.0, WaveMaker has extended its support to allow a dedicated section for the Redshift database.
If you have been working with the Redshift database earlier, which allowed importing as read-only mode, you can now import a Redshift database with read and editable modes. Further, you can customize Redshift tables in the database designer. Perform queries and create variables to compose data that you can incorporate into the UI to display devised data in Charts, List, Data Table, and more.
Connecting to Database
Using the Connect to DB option allows you to import the Redshift database from the Databases menu. WaveMaker takes care of adding the driver dependency in pom.xml.
For instance, in the following image, consider an employee table was imported into the project.
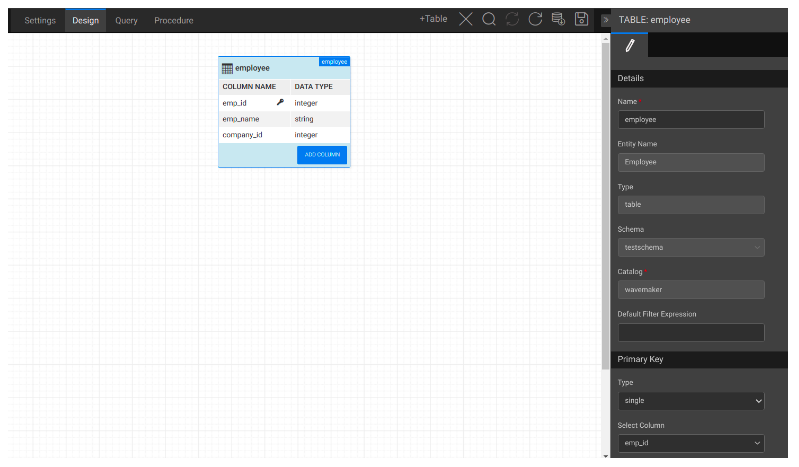
By importing Redshift tables in editable mode, you can create new tables and modify existing tables from the database designer directly in WaveMaker instead of using the Redshift DB console.
Using the above table, you can create List, Data Table widgets, etc., and perform CRUD operations on it.
Querying Redshift Database in WaveMaker
From the Query Editor in the Databases menu, you can run all types of queries and procedures and save them, which you can use to create variables and bind them to the widgets.
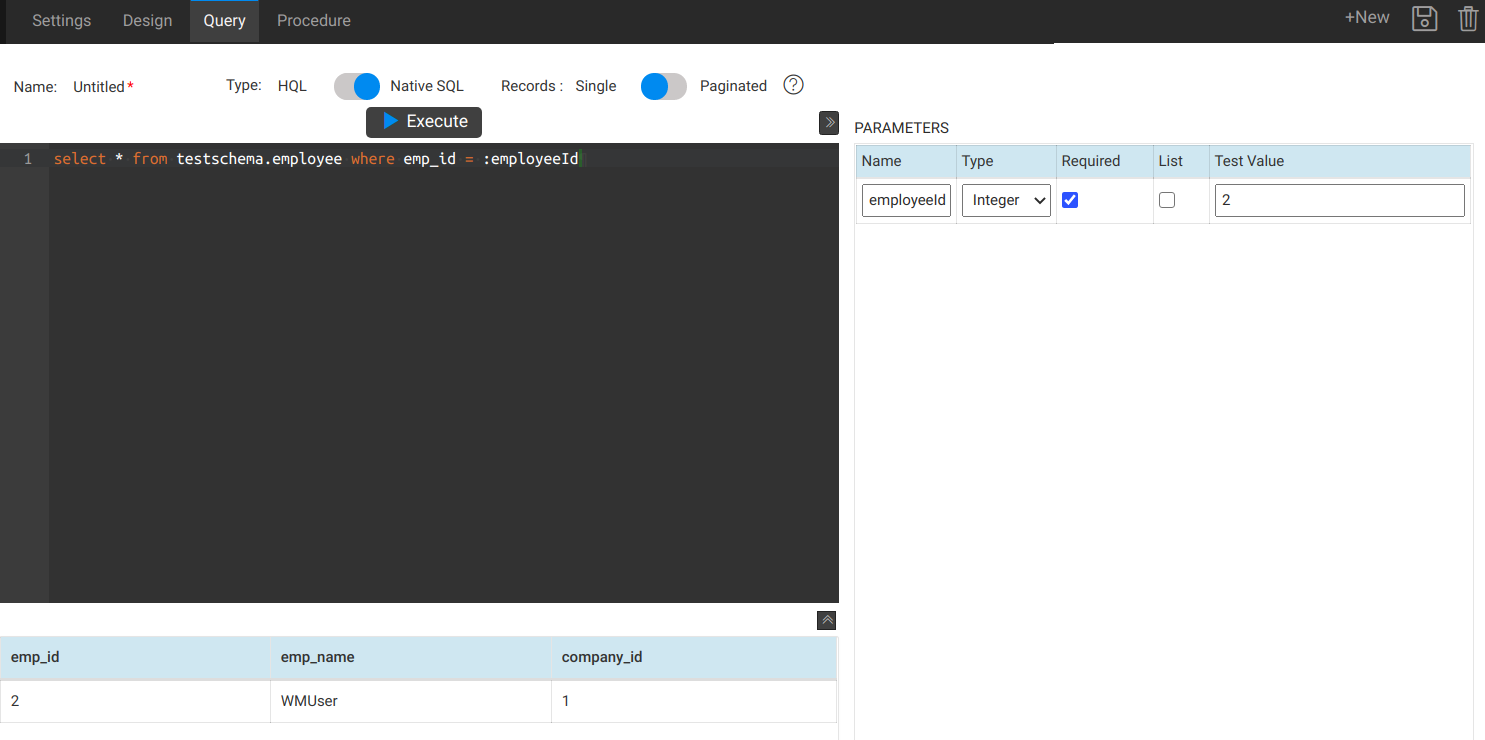
The queries can also have parameters that you can dynamically pass during runtime. Below is an example query of the Employee table that has employeeId as a parameter. For more information, see Working with Queries in WaveMaker.
Using Redshift DB for Creating a List Widget
Drag and drop a List widget and configure the List widget by selecting the same employee table discussed in the earlier points.
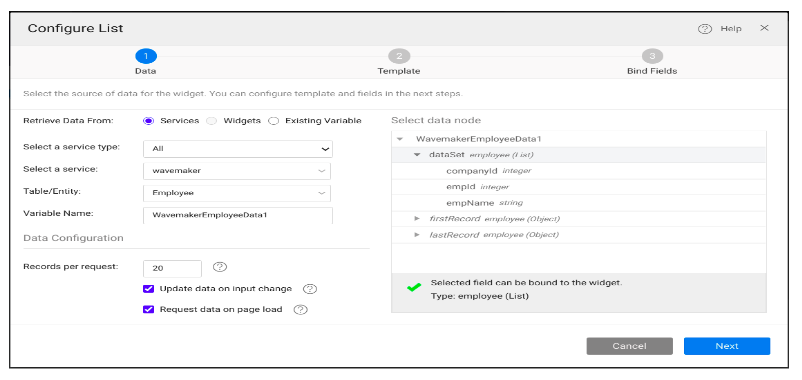
After configuring the widget, you can preview the application and view the table data as a list.
Already using a Redshift database?
Import the Redshift database by following the how-to’s doc Connect To AWS Redshift Database.
In case you don't
Below are the steps to get you started to launch a Redshift cluster:
- Sign in to AWS Management Console. Use the following link to open Amazon Redshift console − https://console.aws.amazon.com/redshift/
- Create a Cluster and select the number of nodes, node capacity, and other database configurations.
- After the cluster creation, you can get the hostname, port, JDBC connection string from the cluster console. Use them to import into WaveMaker.