Working with Queries
There will be times when you want to display data from multiple tables or update/insert values into multiple tables. Queries and Stored Procedures come in handy in such instances. WaveMaker provides editors for Queries & Procedures for integrating them with the WaveMaker applications. Each query & procedure used in the WaveMaker application will be exposed as a REST API for the UI to consume and render the data.
In this section, we will be seeing how WaveMaker supports Query usage with the help of an example.
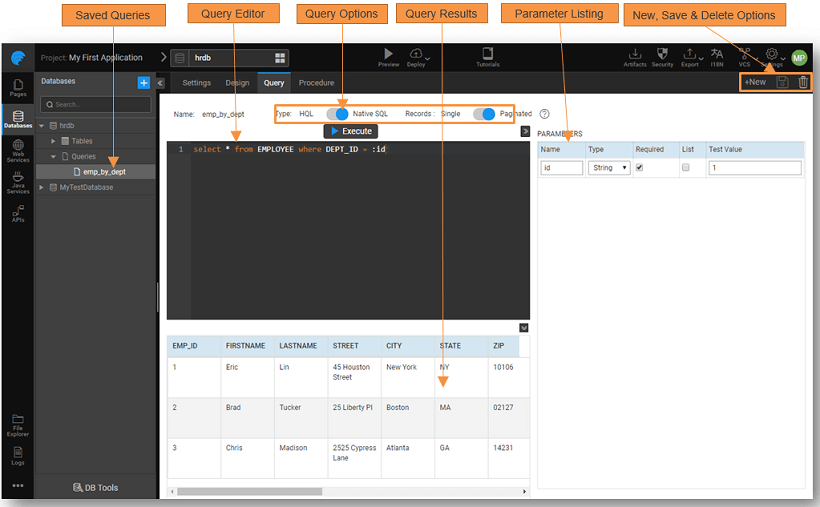
Query Editor
From the Database Designer, use the Query tab to build custom database queries for custom reports and dashboards.
- The editor supports IntelliSense, use CTRL-Space to see suggestions for the table and column names.
- The queries can be in HQL or Native SQL. These queries can be saved and used via the Database APIs generated.
- Parameterised queries are also supported. Parameters can be marked as Required. If marked as required, the Variable associated with this query operation will not be invoked until all the required parameter values are set to the variable input.
- No DB-specific changes, apart from the syntax of the query, needs to be taken care of.
- If the schema name is not the default name, then the table names need to be prefixed with the schema names.
- See here for support on fields of type Blob/CLOB
- You have to Execute the query successfully to be able to save the query. The Save icon will be active only after a successful run of the query.
- Once you save the query, you can see the entry under Database Resources. You can use it to reopen and modify the query if need be. To modify the query, open the query, make the changes, run and save the query. You can also Delete the query using the delete icon.
- When a query is saved, it generates a paginated API that returns a list of objects paginated. In cases where the query returns at most one record, setting the Records to Single will ensure that the generated API returns one object instead of paginated objects. The default is set to Paginated.
- In addition, every API generated for query exposes an additional API for exporting the query results to Excel/CSV. However, in case the query returns a single result, the export API will not be generated. The list of APIs generated can be viewed from the API Designer.
- To execute and access the results of the query within the app, you need to create a Variable based on Database APIs and bind the results to a widget of your choice. Variable Access.
Limitations
- Internal pagination is implemented, as such LIMIT clause in queries WILL NOT be supported
Types of Query
WaveMaker supports two types of queries. They are:
- Native SQL: You can execute Database-specific SQL queries using this option. The same query directly executed in the underlying database. You have to manually escape query in case of spaces, special characters and SQL keywords in the query.
- Hibernate Query Language (HQL): HQL queries depends on Java entities instead of native tables. For more info please refer here.
You can select the appropriate type from the Type option in the designer.
This post explains the usage of queries in WaveMaker using the Native SQL code.
Query Creation
In this example, we will build a query to list the number of vacation days availed by employees from each department. We will be using the hrdb sample database that ships with the product.
- Import the sample database into your project. Database Integration.
- Select hrdb from the Databases Resource to open the Data Designer window.
- Click the Query tab of the data designer window.
- Select Native SQL as the query type and enter the following code in the Query Editor:
select d.NAME, sum(ENDDATE - STARTDATE ) as days
from VACATION v, EMPLOYEE e, DEPARTMENT d
where e.EID = v.EMPID
and e.DEPTID = d.DEPTID
group by d.NAME - Execute the query and see the results in the result box below the query window. Save the query as vacation_days with appropriate description.
Query Usage
We will see how to use the query results by using a Data Table to display the results (you can use any of the Data Widgets for this purpose):
On any page of the project, drag and drop a Data Table widget.
- set Retrieve Data from to Services, this will create a new variable for us
- Select a service type as Database APIs which are auto-generated when you save the query
- Select a service to be hrdb (the database name)
- select Operation/Type as the query saved in the previous step, you will find it under Query Execution group (you might have to scroll down to get to this option).
- Records per request will set the Pagination related options automatically
- Setting the Request data on page load for the Variable ensures that the call to the service is triggered whenever the page is loaded. Setting Update data on input change will ensure the call when the data changes (as seen in the next section).
- Since the query is a select query, the layout option available is Readonly Simple View Data Table.
- You can choose the Pagination style or go with the default.
- You have the option of choosing the fields to be displayed in the grid. Here we will retain the default of displaying all the fields.
Run the project and see the results displayed in the table format.
Create Parameterized Query
Instead of hardcoding values, you have a choice to declare Named parameters in the query. While executing queries these values get replaced with given values. Named parameters can be declared using ":" (colon) prefix. WaveMaker internally uses Hibernate for matching and replacing the named parameters.
For example, let us modify the query above to accept the department name as input and display the results for the specified department name.
- Modify the query created in the previous step to include the parameter for department id. Or you may create a. new query thus:
select d.NAME, sum(ENDDATE - STARTDATE ) as days
from VACATION v, EMPLOYEE e, DEPARTMENT d
where e.EID = v.EMPID
and e.DEPTID = d.DEPTID
and d.DEPTID = :did
group by d.NAME - The parameter entry is made in the Parameters section.
- Since this query will return a single record set Records to Single.
- Select the appropriate data type for the parameter using Type field, enter a Test Value and Execute the query. Use List in case your parameter takes multiple array value, the test values in such a case should be comma-separated values without spaces. For example, in this example if did were a list then the test values would be 1,2.
- The parameters can be set to server-side properties like current date, time, id, or username by picking the same for Type from under the Server Side Properties drop-down. When you select this option while executing the query the appropriate value is taken from the application rather than from the user.
For example, if you have a query:You can, in the Parameter section, set the parameter id Type to LoggedIn UserId from under the Server Side Properties. When you enable security using the database as the service provider and employee as the User table, then setting the id to LoggedIn UserId will get the user id of the current logged in user. You need not bind the parameter again, explicitly.select FIRSTNAME
from EMPLOYEE where EMP_ID = :id - Parameter values can also be set to App Environment properties and be defined separately for different app environments (know more).
- To execute and access the results of the query within the app, you need to create a Variable based on Database APIs and bind the results to a widget of your choice. Variable Access
Using Parameterized Query
- Create a Database Crud Variable for Department table. Variable Access
- Add a Select widget to the page and bind it to the Variable dataset created in the previous step with the department name as the Display field and department id as the Data field. This will serve as input to the Query. Know more about Select Widget usage.
- On the same page below the Select Widget, drag and drop a Data Table widget
- set Retrieve Data from to Services, this will create a new variable for us
- Select a service type as Database APIs which are auto-generated when you save the query
- Select a service to be hrdb (the database name)
- select Operation/Type as the query saved in the previous step, you will find it under Query Execution group. Make a note of the Variable name generated.
- Records per request will set the Pagination related options automatically
- Check Update data on input change and uncheck Request data on page load, since we want the query to be executed after the user has selected a department.
- Since the query is a select query, the layout option available is Readonly Simple View Data Table.
- You can choose the Pagination style or go with the default.
- You have the option of choosing the fields to be displayed in the grid. Here we will retain the default of displaying all the fields.
- Access the variable created during the configuration of the Data Table. It will have Data tab which can be used to bind the input value for the parameter. Bind it to the datavalue of the select widget created in step 3, while Data Table drag and drop.
- Run the project.
- Select various departments and see the values in the Data Table change.
Query Operation Type
For all queries, there will be a Rest API generated. Depending on the type of the query, the appropriate HTTP method will be generated. You can access them from the API Designer. Here is the mapping for the type of query vs operation type:
- SELECT:
GET - INSERT:
POST - UPDATE:
PUT - DELETE:
DELETE
When you use Test in filter API, you must follow the exact naming convention as specified on column names used in the query params of generated APIs.
Example:
- Go to API designer, select hrdb (from sample databases), and click Department table.
- Select POST/filter API.
- In the Test tab, for the q parameter, the sample value should be as follows:
- Correct way:
name = 'Engineering' - Incorrect way:
Name = "Engineering"
- Correct way:
Boolean values should either be 'true' or 'false', and it cannot be '1' and '0' respectively.
Example:
Sample Input query params in the filter API for a Data Table that contains Boolean type should be as follows:
Correct way:
- patientId = 1313 and status = true
- patientId = 1313 and status = false
Incorrect way:
- patientId = 1313 and status = 1
- patientId = 1313 and status = 0
Query Architecture
For all queries and procedures, there will be a Rest API generated with the Service layer. Along with the API, depending on the query or procedure type, request and response POJO classes are generated.
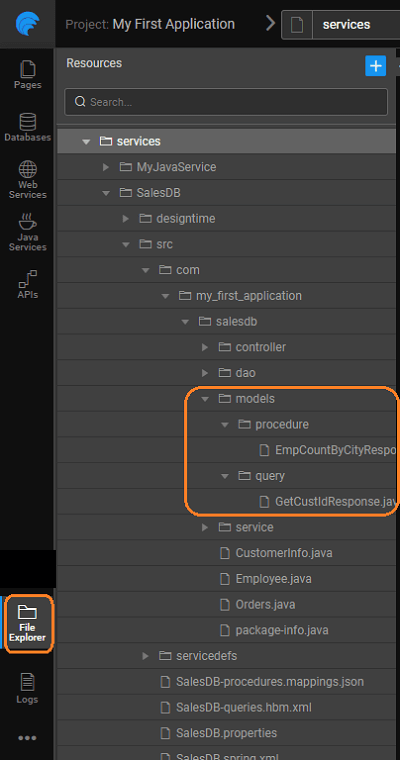
Understanding generated Code File structure
Models
Both Request and Response POJO classes are generated as: <queryName>Request/Response
- These classes are generated in a package: <service_package>.models.query
- Response class is generated only for SELECT queries. The return type for Non-Select queries will be integer hence POJO class is not generated.
Example:
query with name getAllEmployees will generate GetAllEmployeesResponse class with all returned columns. - For HQL queries existing Model classes will be used if possible, else a Response model similar to Native queries will be generated.
- Example-1
queryfrom Employee;
This will return only Employee object hence it will use the existing Employee type (as generated for Data table) instead of creating a new one. - Example-2
select e.empId, e.department from Employee
In this case, the response contains different fields so a new type will be created as <queryName>Response with fieldsempIdanddepartment.
- Example-1
Here, department is a related field with type Department, so generated POJO uses existing Department type.
- Request class is generated only for INSERT and UPDATE queries.
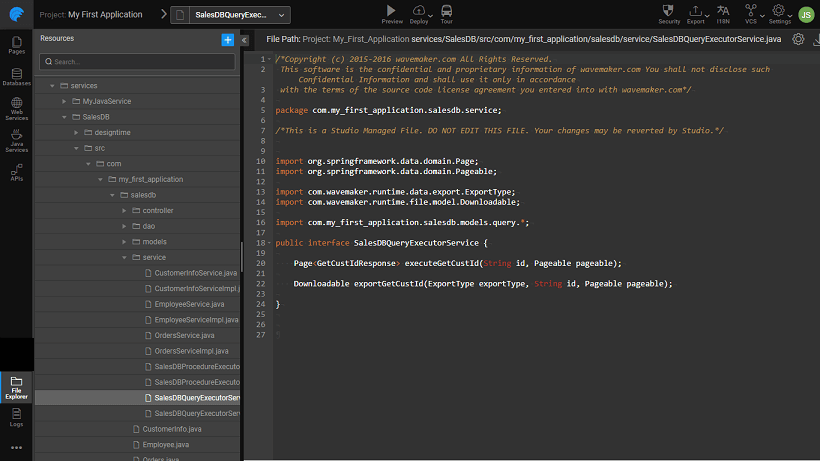
Services
This layer exposes the methods related to the configured query and procedures. Controller layer uses these methods to complete the user requests. We recommend using methods from this layer in custom Java services.
- Class with name
QueryExecutorServiceis generated in the package<service_package>.serviceFor eg: for Servicehrdb, class name will beHrdbQueryExecutorService - Method with name
execute<queryName>will be generated for all configured queries- For SELECT and DELETE queries, all parameters are configured as arguments for that method. In the case of Paginated request Pageable argument is added to the method signature.
- For INSERT and UPDATE queries,
<queryName>Requestis the argument. - For all SELECT queries
<queryName>Responseobject is returned. In case of Paginated, returnsPage<<queryName>Response>. - In the case of HQL query and queries returning existing types, the return type will be the existing type.
- For non-select queries, it returns INT.
- Export API is added for queries which will return Paginated data. Method name will be
export<queryName>and which takes same arguments as execute method (as mentioned above).
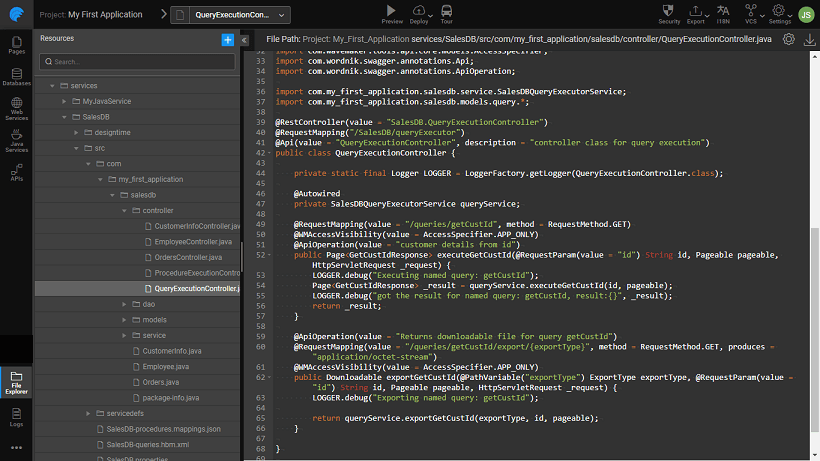
Controllers
- Separate controller classes are generated for query and procedures with names as
QueryExecutorControllerandProcedureExecutorControllerrespectively in package<service_package>.controller. - Rest API is generated for each configured query and procedure. Generated method signature will be same as service layer method signature.
- For methods returning INT type, controller layer returns
IntegerWrapper.