Pages Concepts
Introduction to Pages in WaveMaker low-code platform.
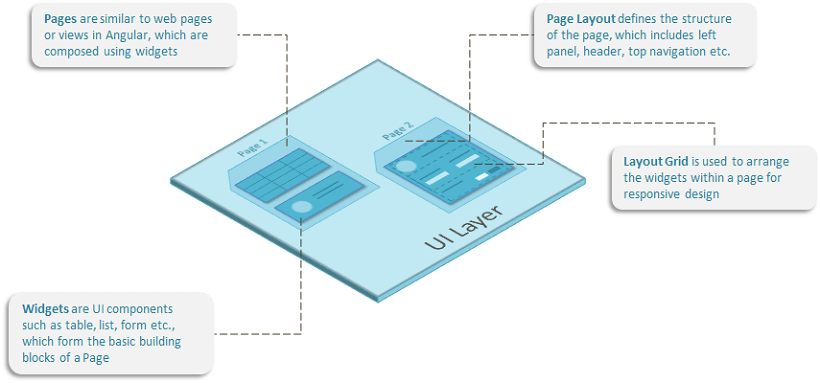
An application is a collection of pages. Each page is composed of different UI elements and Widgets. These UI elements enable user interaction with the app and can get data from the backend services. You can be set navigation and interaction rules across pages.
To design pages, see the Design Overview section.
You can navigate to the pages section as shown in the image below.
How Pages work
WaveMaker Pages are built using the drag-n-drop approach, by placing widgets in the corresponding responsive layout grids.
Page Architecture
In this document, you will learn about the following:
- WaveMaker apps as single-page applications.
- What a typical page life cycle of a WaveMaker app looks like.
WaveMaker as a Single Page Application
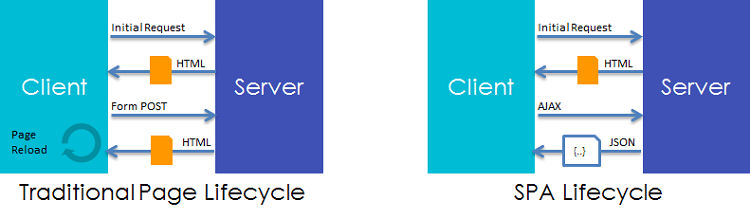
Single-Page Applications (SPAs) are Web apps that load a single HTML page and dynamically update that page as the user interacts with the app. This is achieved through a clear separation of front-end and backend through AJAX Service, thus cutting full roundtrip to the server to retrieve new presentation content (HTML) which is common to traditional page life cycle.
A WaveMaker application is a single page application(SPA). Though an app is composed of multiple pages, these pages are loaded asynchronously on demand. At a given point of time, a single page is loaded in the browser for the user to see and interact. The structure of the page i.e. header, footer, left nav is retained across pages, causing no jitter.
A page can be composed of:
- Widgets which are loaded as part of the page, or
- Partial Pages as the content of container widgets like Panel, Tabs, Accordion, etc.
Page Life Cycle
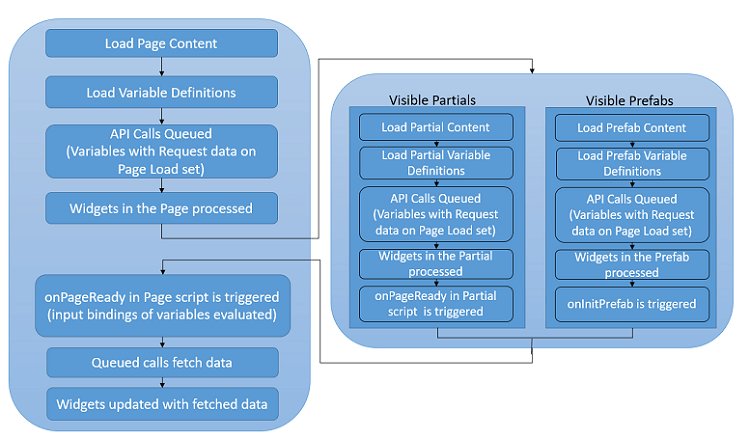
When the request for a page is made, it goes through the following life-cycle:
- The network request for the page content is made and the Markup, CSS, JavaScript and Variables for the page are loaded.
- The Markup is then processed and compiled. During Markup compilation, if any Container widget with partial as content is found, then
- the resources corresponding to that partial are loaded,
- the onPageReady callback method in the partial script is invoked. By this time the Widgets and Variables in the partial are loaded and can be accessed in the script. Note: the app scoped variables are loaded when the app starts, here we are referring to the page scoped variables alone.
- The above step is repeated for all the partials and Prefabs found within the page.
- Once all the partials are loaded, the onPageReady callback method in the page script is invoked. At this point, all the Widgets and Variables in the page are ready.
- Variables, in the page and in the loaded partials, with Request data on page load set to true are triggered at this point. The Variables will not have any data at this point. They are only loaded in memory. The data fetched by these Variables can be accessed in their respective callback methods (onSuccess, onResult, etc.).
Flow Diagrams
Page without any partials or Prefabs 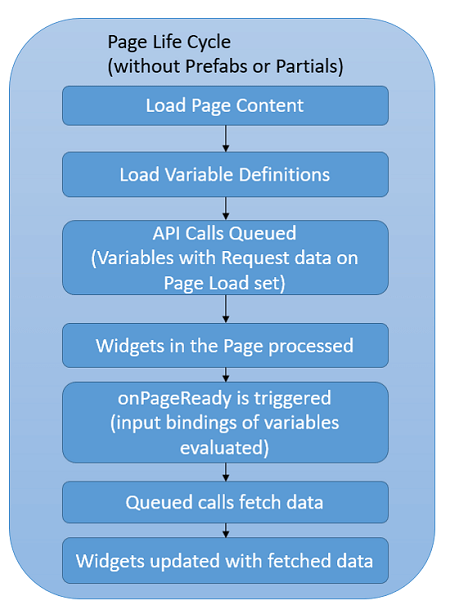 Page with partials and Prefabs
Page with partials and Prefabs