Temporal Support
DB2 has an inbuilt support for temporal or time-based data management. The temporal features in the DB2 product enable you to accurately track information and data changes over time and provide an efficient and cost-effective way to address auditing and compliance requirements, without having to specifically code for the same.
WaveMaker extends support for auditing and history using DB2 Temporal. You can seamlessly integrate the temporal functionality within WaveMaker apps and take advantage of DB2’s in-built time-based data management. In this document, we elaborate how WaveMaker achieves this support. For a use case example, refer to this document.
Understanding Temporal
Temporal allow the insertion, update, deletion, and query of data in the past, the present, and the future while keeping a complete history of "what you knew" and "when you knew it".
There are three types of temporal tables supported by DB2:
System-period temporal tables
System-period temporal tables to allow for tracking the updates and deletes to the table rows over a period of time. This is achieved through:
Application-period temporal tables
Application-period temporal tables help in tracking business time i.e. when certain business conditions are, were, or will be valid. This is achieved through:
Bitemporal tables
Bitemporal tables manage both system time and business time and combine all the capabilities of system-period and application-period temporal tables.
For more details on DB2 Temporal refer to A matter of time: Temporal data management in DB2 10.
Temporal Support in WaveMaker
When a DB2 database is imported, WaveMaker identifies the data tables with Temporals and allows for extraction of history data for those tables.
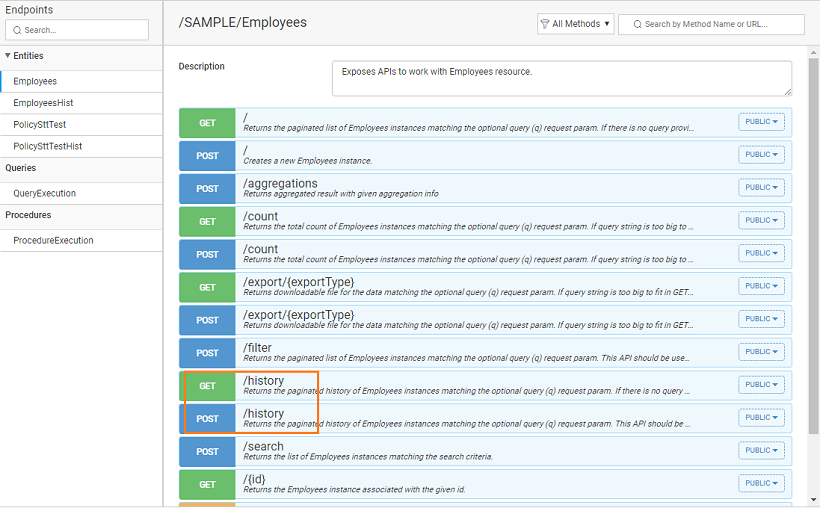
Two types of APIs are generated for temporal tables:
- The standard APIs for CRUD operations and other functionalities like count, find, filter etc. These APIs can be used to deal with data that is valid at the current time i.e. at the time of application run.
- The period APIs to fetch data for
- a time different from the current time, or
- for a specific time period.
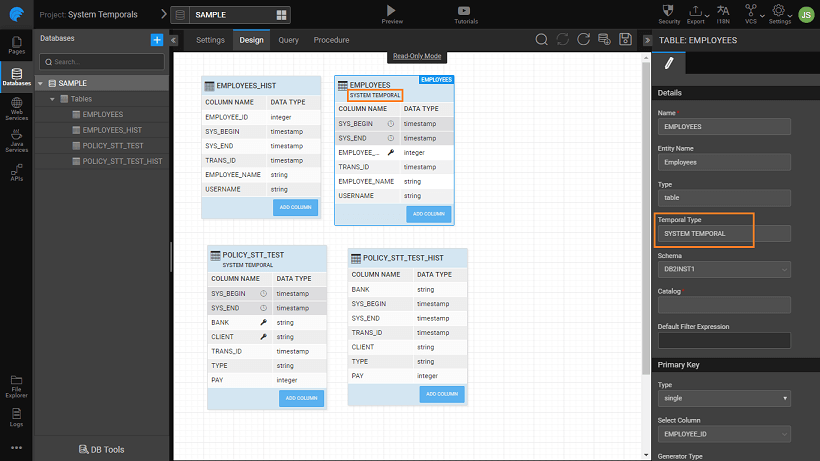
Database Designer
- In DB designer a table property specifies the table Temporal Type as:
- System Temporal,
- Application Temporal, or
- Bi Temporal
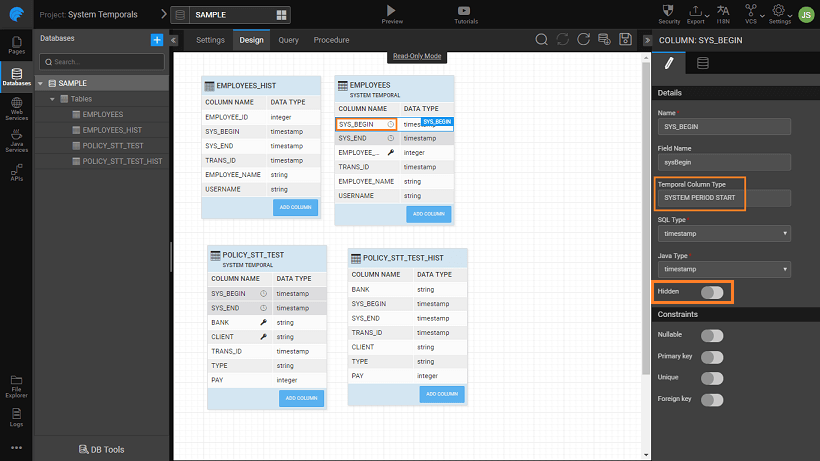
- A column property, Temporal Column Type, specifies the temporal type and the period type. The values can be:
- System Period Start
- System Period End
- Application Period State
- Application Period end
- A clock icon will be displayed against columns which are part of temporals. These fields will not be displayed in the query results. You can uncheck the Hidden property in order to view these fields in the UI.
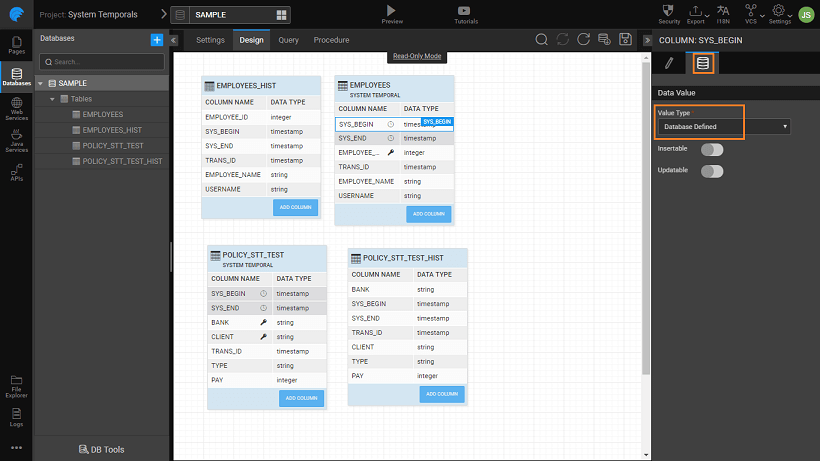
- By default system period columns and transaction id are marked as Database defined. The values need not be entered by the user, they will be auto-populated by the database.
Generated REST APIs
Two types of REST APIs are generated for the DB2 Temporal tables:
Standard CRUD and additional functionalities.
Following conditions are applied for application temporal tables while requesting database.
Period APIs
In addition to the standard APIs generated for the imported databases, the tables with temporals will have an additional period APIs auto-generated. This can be used to access the temporal data.
periods This API returns the history data for the temporal table by applying given filters.
Method: GET or POST Parameters
- systemPeriodStart [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 01-01-1901.
- systemPeriodEnd [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 31-12-9999.
- applicationPeriodStart [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 01-01-1901.
- applicationPeriodEnd [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 31-12-9999.
- q [optional]: query to filter the history data.
- Pageable [optional]: pagination information.
- /periods/{id} (or) /periods/composite-id This Api returns the history data for given id and by applying given filters.
Method: GET Parameters
- Id columns information as specified for normal findById API.
- systemPeriodStart [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 01-01-1901.
- systemPeriodEnd [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 31-12-9999.
- q [optional]: query to filter the history data.
- Pageable [optional]: pagination information.
Update & Delete API
For tables having Application temporals, these APIs will be generated. These API’s will make use of DB2 portion of syntax to update/delete the history.
- /periods Method: PUT This API used to update the history data for Entity with given application temporal clause and q to filter.
Parameters:
- applicationPeriodStart [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 01-01-1901.
- applicationPeriodEnd [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 31-12-9999.
- q [optional]: query to filter the history data.
- Type: Body: Entity data to update.
Returns:
This API returns IntegerWrapper, with affected rows count. Method: DELETE This API used to delete the history data for Entity with given application temporal clause and q to filter. Parameters:
- applicationPeriodStart [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 01-01-1901.
- applicationPeriodEnd [optional]: exists in case of system temporal tables; period value should be in Timestamp format, default value: 31-12-9999.
- q [optional]: query to filter the history data.Returns: This API returns IntegerWrapper, with affected rows count.
- composite-id/periods Method: PUT This API used to update the history data for Entity with given application temporal clause.
Parameters:
- id’s [optional]: Id columns as specified in normal Update API.
- Type: Body: Entity data to update.
Returns:
This API returns IntegerWrapper, with affected rows count. Method: DELETE This API used to delete the history data for Entity with given application temporal clause.
Parameters:
- id’s [optional]: Id columns as specified in normal Update API.
Returns:
This API returns IntegerWrapper, with affected rows count.
Library Enhancements
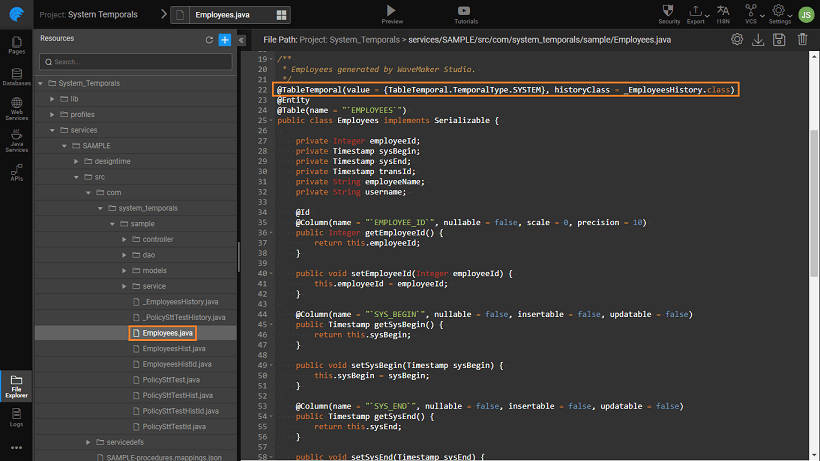
To achieve the above functionality, a @TableTemporal annotation is added, specifying the table temporal types on that Entity/Table. This information is used while making the database request. This annotation requires temporal types array. Temporal Types can be:
- SystemTemporal - Tables having System Temporal will be annotated with this annotation.
- ApplicationTemporal - Tables having Application Temporal will be annotated with this annotation.
Though there are no API changes in WMGenericDao, while processing request the above annotation will be used.
Limitations
- DB2 database is imported as a Read-Only schema. As such, no changes to the table schema is allowed from the platform. Any changes need to be made to the database and the database re-imported for the changes to be reflected in your WaveMaker app.
- Update of rows for Portion of a business time period is not currently supported.