Integrate Database Service in JavaServices
WaveMaker generates REST API when a database is imported. However the lower level database access can be used inside a Java class to execute custom business logic. In case if you want more control on database service methods or if you would like to extend or use the database service API's or methods based on business logic then you can @Autowire the Service class of that particular database entity.
The autowiring feature of spring framework enables you to inject the object dependency implicitly. The advantage of autowiring is, it requires the less code because we don't need to write the code to inject the dependency explicitly.
Accessing Database services using Java Service
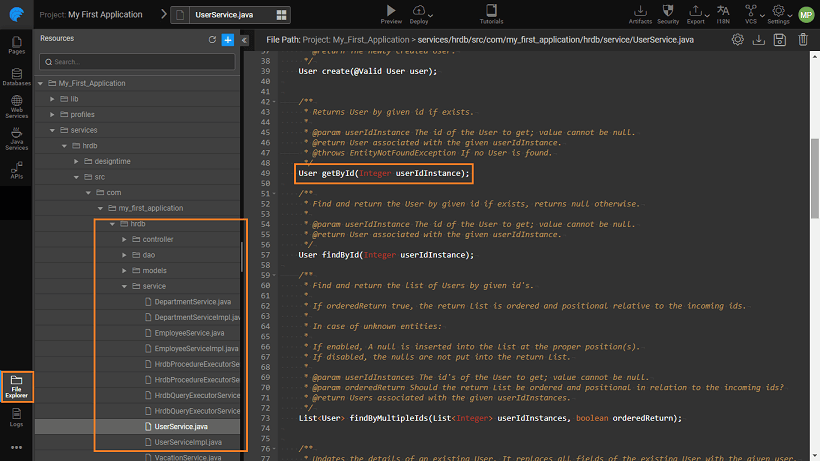
To access a database table from a Database Integrated into your app, you need to access the Java Service file corresponding to the table from the Services tab in the left panel. For example, to access the User table from hrdb, you need to access the UserService.java file from the services folder available under FileExplorer panel.
Where to find DB Services
You can find a list of methods for User table in userservice.java like create, delete, find, update, query service, procedure service, and more.
Accessing DB Services
For working with the Database table operations such as insert, get, update in Java Service, the following generic code can be used.
Here we are trying to access the User table from the sample hrdb:
In the above example, the value for the parameter query for findAll method in the service should be an HQL query string.
Example: role='adminrole' and tenantId=1
Accessing different DB Services with the same name
If there are two or more beans for same class type, you need to use @Qualifier annotation along with @Autowired annotation and pass the bean name in annotation parameter.
For example, you have more than one implementation of UserService, then use qualifier to inject the specific implementation of User service.
Database Transactions from Java Service
Transactions for related entities
Transactions can be used in cases where you have multiple independent statements which need to be linked together. A transaction can end in two ways: with a commit or with a rollback. When a transaction commits, the data modifications made by its statements are saved. If a statement within a transaction fails, the transaction rolls back, undoing the effects of all statements in the transaction.
Let us see a simple example of interacting with the hrdb database in Java service using Transactions.
- Define an API that creates employee and retrieves the same from the database.
- Create employee and retrieving employee are two independent calls to the database. When we enclose it with the transaction it will ensure that either both actions occur or neither action occurs.
- In the below transaction code, if createEmployee is successful but retrieve employee fails, then created employee will be reverted from the database.
To see the rollback in action replace the last line with:
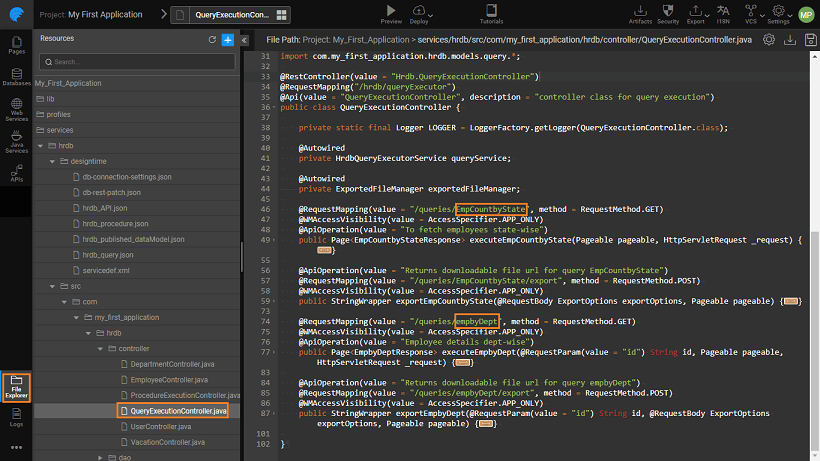
Accessing Query services using Java Service
Named Queries or queries that are written, tested and saved in query editor of Database Designer. Query Editor.
For each and every named query, there will be a rest service generated from query execution controller and exposed under APIDesigner panel. Here we are seeing two queries - EmpCountByState and which were created from the query editor.