Database CRUD Operations Event Listeners
When you create a new database or import an existing database in WaveMaker, the WaveMaker platform generates the database service inside the WaveMaker application.
The database service code that gets generated inside the application is layered, as shown below.
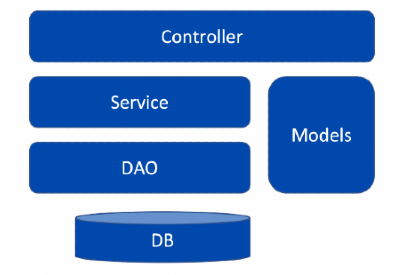
Layered Architecture
Controller Layer
The Controller Layer is responsible for the HTTP request and response processing, converting to and from JSON to Java Object, etc. The Controller layer code is annotated with the Spring REST API annotations.
Service Layer
The Service layer is responsible for static validations, transactional boundaries and invokes the respective DAO methods for object persistence.
DAO layer
The DAO layer is responsible for communicating with the database. It maintains a pool of connections with the database and uses Hibernate ORM for persistence.
Generated Code and Syncing Database
The generated code is always in sync with the database schema. If any changes are made externally to the database schema, the respective database must be reimported, thus making the code regenerated to keep the code & schema in sync.
The platform manages the generated code, and therefore it does not allow any modifications to it or add the custom business logic.
Database CRUD Operations
In most cases, the application developers should have control on the database CRUD operations to perform the following scenarios:
- Dynamic Validations
- Custom Business Logic
- Authorization checks / Row-level security
- Encrypt or Decrypt the field values
- Set default/override values during insert/update
- Invoke additional services for integration
- Audit history for the data changes etc
The generated code is not editable to include the above use-cases when performing database operations.
To address all the above use-cases, WaveMaker introduces Event Listeners for the typical database operations.
Listen and Handle Events
WaveMaker’s application runtime framework publishes the entity CRUD event during the respective database operation. Each of the operations, aka Create, Read, Update and Delete, publishes two events - they are pre and post-operation events. The WaveMaker application developer should listen to the “interested” events and handle the respective events in a Java Service.
Each event extends EntityCRUDEvent. The class has methods to get the serviceId and entityClass for which the event is generated.
The events can be listened to using the @EventListener or @TransactionalEventListener annotations.
List of Events for CRUD Operations
EntityPreCreateEvent
Published before creating an entity in the database. This event will get the handle of the entity object being created.
EntityPostCreateEvent
Published after creating the entity in the database. This event will get the handle of the entity object created.
EntityPreUpdateEvent
Published before updating the entity in the database. This event will get the handle of the entity object being updated.
EntityPostUpdateEvent
Published after updating the entity in the database. This event will get the handle of the updated entity object.
EntityPreDeleteEvent
Published before deleting an entity from the database. This event will get the handle of entityid, which is to be deleted.
EntityPostDeleteEvent
Published after deleting the entity from the database. This event will get the handle of the entity that is deleted.
EntityPreFetchListEvent
Published before fetching the list of records from the database. This event will get the handle of the query string used for filtering the entities.
EntityPostFetchListEvent
Published after retrieving the list of records from the database. This event will get the handle of the pageable response.
EntityPreFetchEvent
Published before fetching a record from the database. This event will get the handle of the entity ID.
EntityPostFetchEvent
Published after fetching a record from the database. This event will get the handle of the entity object.
Imports
Below are some of the class imports used in the examples shown below
Events Listeners with Examples
Below are some examples of listening to events, assuming sample HRDB is added into the project, with four tables, including User, Department, Employee, and Vacation. You can include the code snippet given below in any of the Java services in the application.
Handling Business Logic During User Creation Process
- To listen to each entity, you need to write a separate method using the respective Generic as the parameter in the method.
- Any exception thrown from the above method will stop the create operation, and the error message will be sent to the caller.
Listen to User Post Creation Event
- To listen to each entity, you need to write a separate method using the respective Generic as the parameter in the method.
- The code written in the EventListener for postCreateEvent will participate in the same transaction as the create operation. Hence any exception thrown from this method will roll back the create operation, and the exception message will be sent to the caller.
Listen to User Creation Event only on Successful Transaction Commit
- To listen to each entity, you need to write a separate method using the respective Generic as the parameter in the method.
- The code is written in the @TransactionEventListener(phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_COMMIT) for postCreateEvent will be executed only after the successful transaction commit of the create operation.
- Any exception thrown from this method will not have any impact on the create operation. However, the exception message will be sent to the caller.
Listen to All Entities Creating Event Listeners with Exception for Generic Types
To listen on all entities creating event listeners, remove the generic type in the Event Listener’s method declaration. This can be helpful to achieve cross-cutting concerns like operations logging or metrics collection or common validations across all entities.
- This listener will be called when an entity of any type is created in the database.
- In case if there are multiple databases imported, this method will be called for all those entities across all the imported databases.
- It is recommended to use the respective entity-specific events unless you want to handle the common logic same across all entities.
- Any exception thrown from this method will stop the create operation and the exception message will be sent to the caller.
Listen to Events with Different Event Listener Annotation Declaration
Suppose you have multiple database services in the application and want to listen to only one of the service’s all entity events with only different event listener annotation declarations. In that case, you can add a new condition attribute to event listener annotation.
This listener will be called when an entity of any type is created in the database that matches the given condition. It is recommended to use the respective entity-specific events unless you want to handle the common logic same across all entities. Any exception thrown from this method will stop the create operation, and the exception message will be sent to the caller.
Update and delete events work similarly with update having the entity information in its event object and deleting the entityId information in its pre-event object.
Use Cases
Record Transactional History of an Entity
Performing Dynamic Validations using CRUD Listeners
Custom Business Logic using DB CRUD Event Listeners