Record Transactional History of an Entity
In this document, learn how you can use Database CRUD Listeners to record the history, including the details related to data change of a specific entity/table in a logger table.
In the following example, we use three Event Listeners, including:
Download and Import Database File
- Download the EmployeeDB SQL file.
- Import the file in DB Tools.
- Connect to the Database from your application.
Create a Java Service to Insert Transactional Details
In this use case, we use the EMPLOYEE_DETAILS_LOG table to insert transactional details of the EMPLOYEE table.
- Create a Java service in the project.
- Add the below import statements.
Add Methods to the Java Service
Add the following three methods into the Java service that perform the below operations:
- Get the logged-in user details from the security service,
- Get employee details from the event, and
- Insert employee details into the
EMPLOYEE_DETAILS_LOGtable.
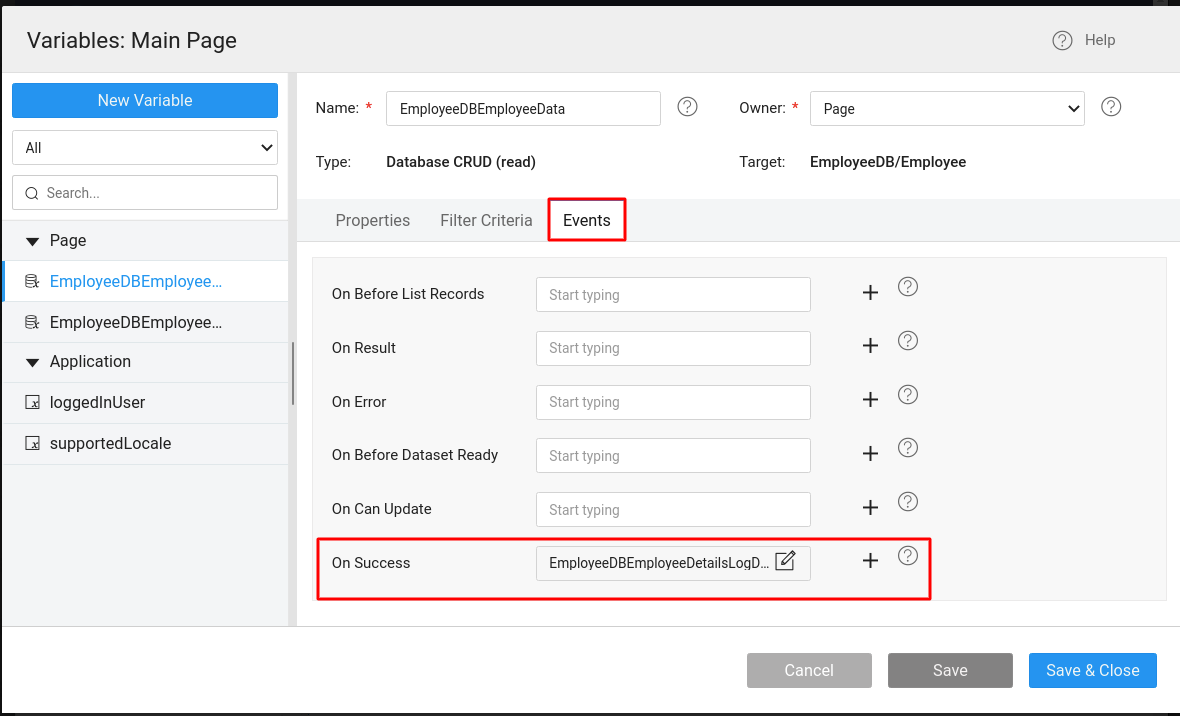
Configure the Variable to Data Table
- Go to a page, and drag-and-drop a Data Table widget.
- Create an
EMPLOYEECRUD variable and bind it to the Data Table at the time of configuring the widget. - Drag and drop another Data Table widget.
- Create an
EMPLOYEE_DETAILS_LOGCRUD variable and bind it to the Data Table when configuring it. - Invoke the
EMPLOYEE_DETAILS_LOGCRUD variable using theonSuccessevent of theEMPLOYEECRUD variable created in step-2.
Preview the Application
In preview, perform some CRUD operations in the Employee table and notice the transactional details insert into the EMPLOYEE_DETAILS_LOG table.
See Also
Database CRUD Operations Event Listeners
Dynamic Validations using CRUD Listeners
Custom Business Logic using DB CRUD Event Listeners