CRUD Variable for REST Services
For every service imported into the app, the APIs exposed by the service can be accessed to perform many operations with it. A variable needs to be created to invoke the service and store the results of that invocation. The Variable operations are restricted by the offerings of the underlying service.
WaveMaker automatically generates UI functionality for create, read, update, delete (CRUD) operations if you import REST API endpoints via Swagger/OpenAPI. For more information, see Import REST APIs via Swagger.
A comprehensive list of these APIs can be found from the API Designer after the import of the service.
Since the service needs to be invoked to fetch the data, the widgets bound to these variables will display values only at run-time, not in Studio mode.
Supported Widgets
Web: DataTable, Form
Mobile: List with Form
How to Create a CRUD Variable
You can create a CRUD variable by using the following two approaches.
- Create a CRUD variable from a Variable Dialog.
- Create a CRUD variable by drag-n-drop of the supported widget.
Using Variable Dialog
- Select Variable from the workspace toolbar.
- Click New Variable from the Variable Dialog.
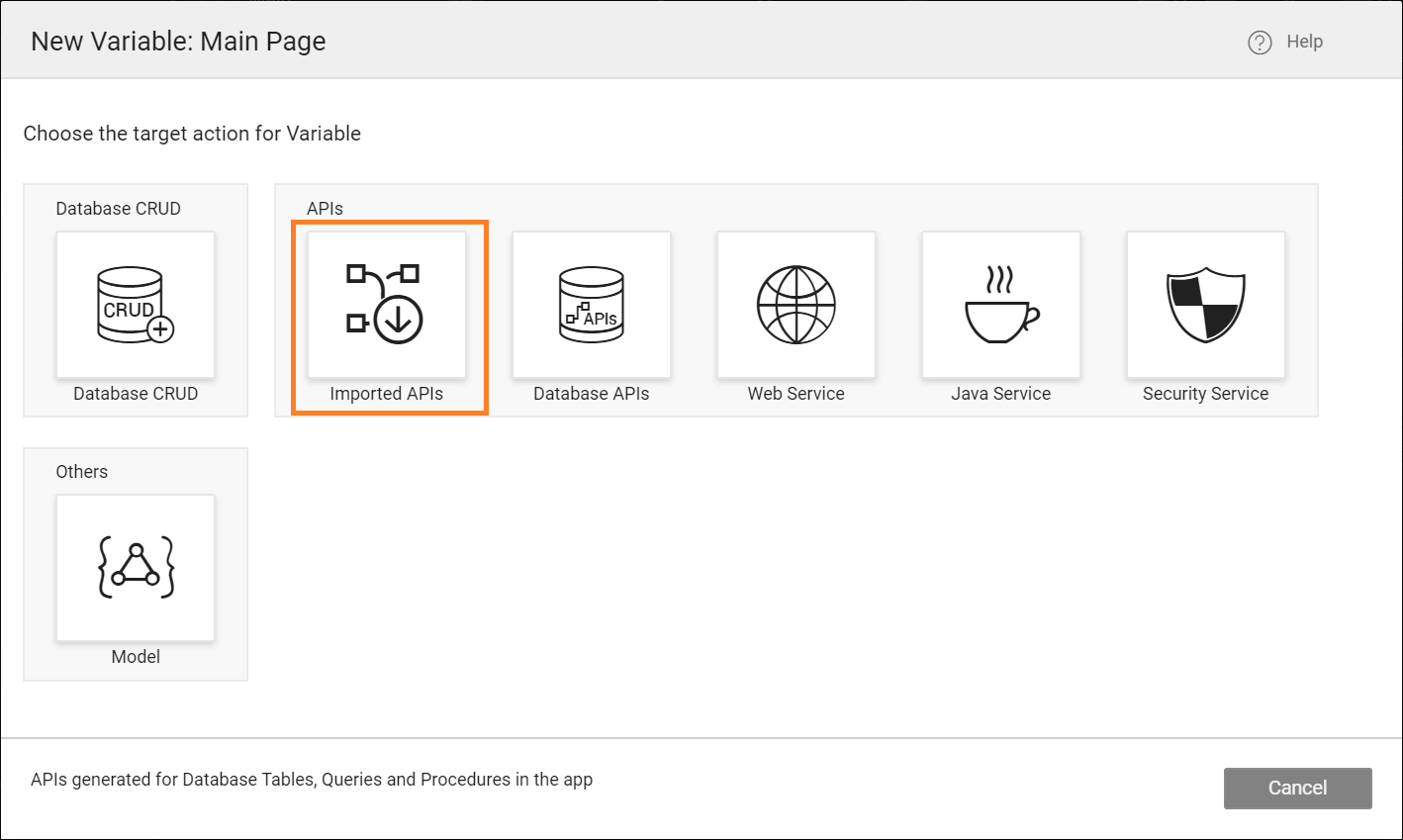
- Select Imported APIs as a target action for the Variable.
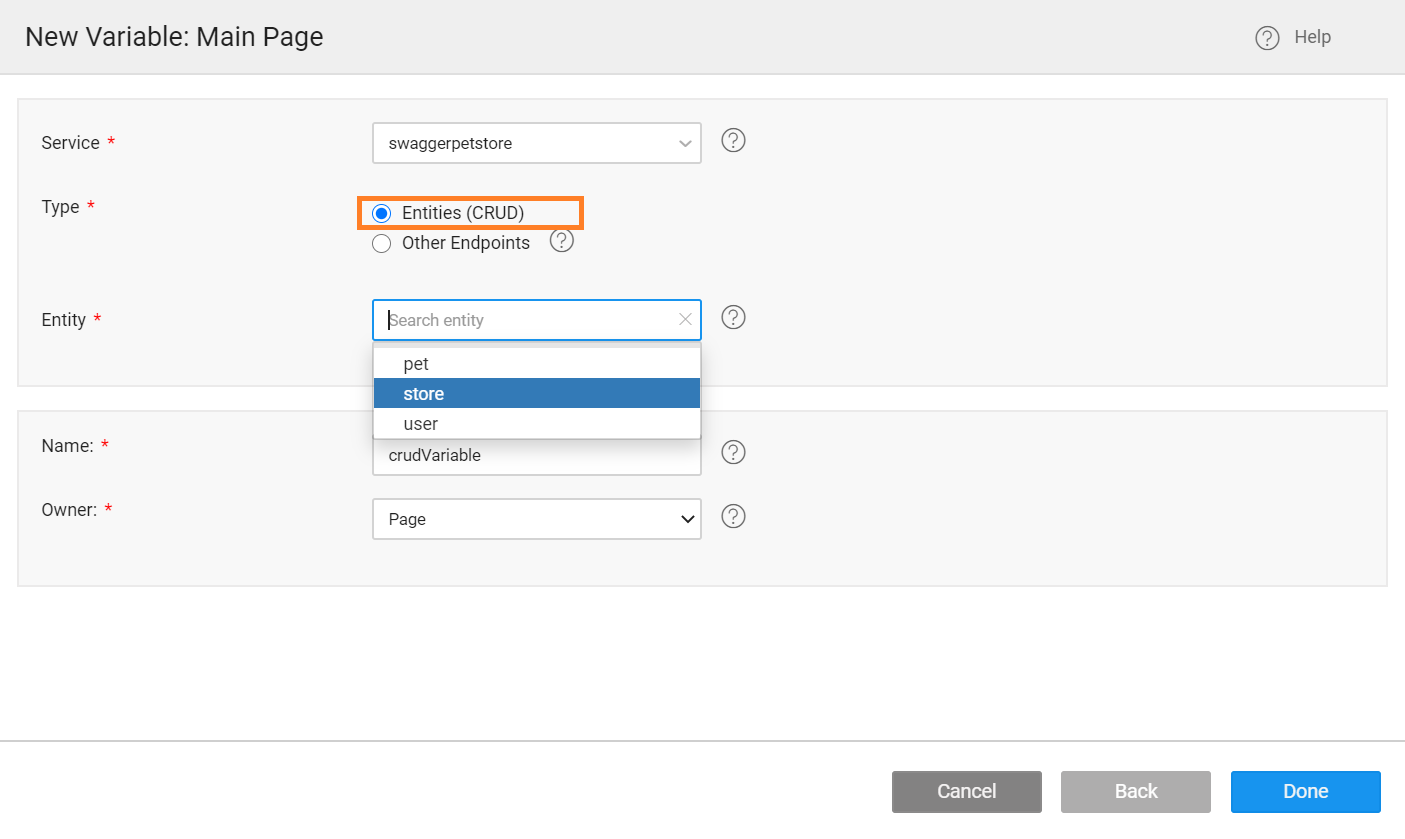
- In the new Variable dialog, configure the properties for the variable.
You can create a service variable to perform one operation at once using Other Endpoints. For more information, see Service Variable for Imported APIs.
- Service: Select the Imported Service.
- Type: Select the Type as
Entities (CRUD). - Entity: Select the entity from the dropdown. Create, Read, Update, and Delete methods group into a single entity. For more information, see Entity and Endpoints.
- Name: Set by default, but you can modify it.
- Owner: The scope of the Variable. Page is the default option. You can choose Application to make the variable available across the app.
- Click Done to complete the variable creation process.
Using Drag and Drop of Widget
Drag and drop the supported-widget on the canvas. For example, in the following image, a Datatable widget is used to create a CRUD variable.
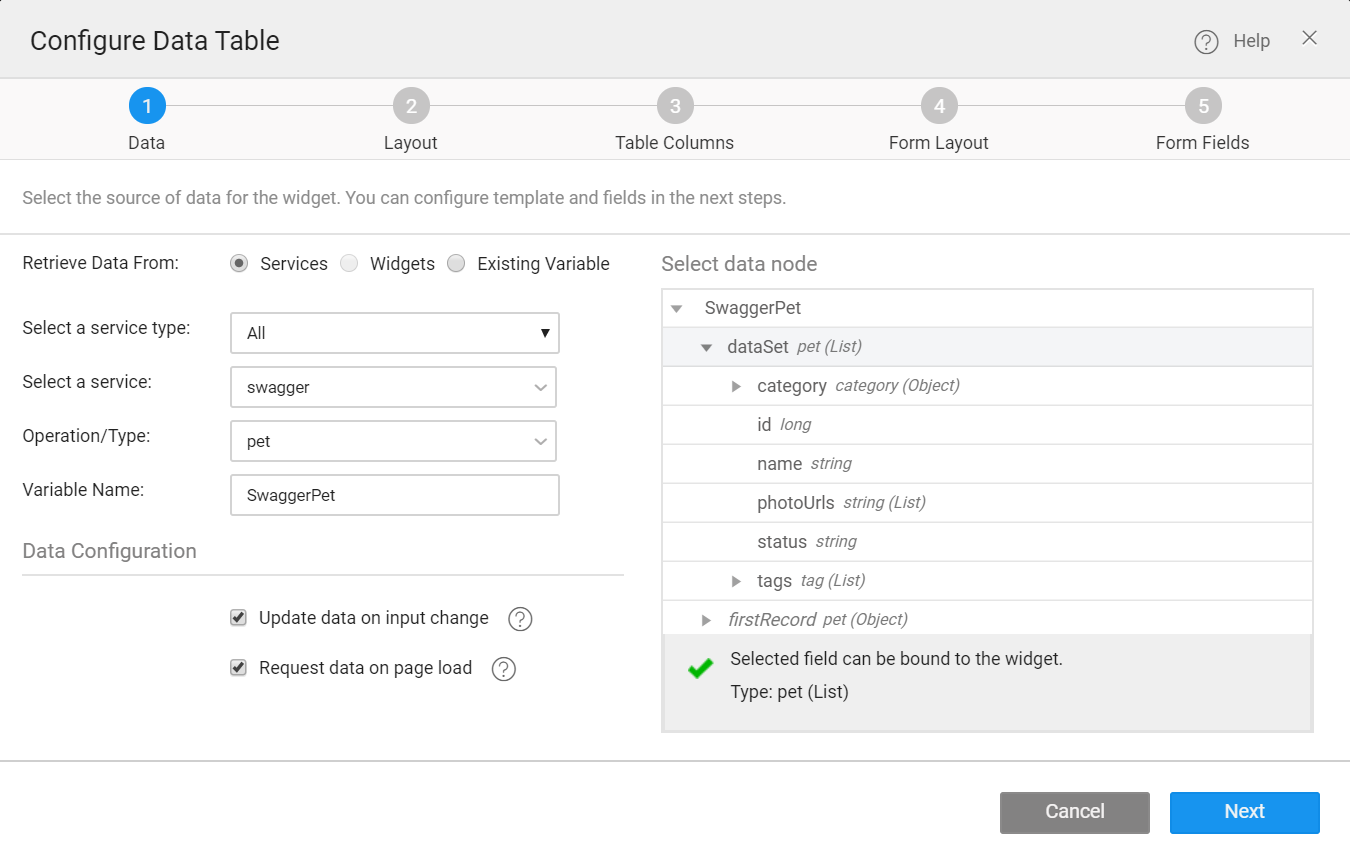
- Retrieve Data From: Services is selected by default.
- Select a Service type: To use CRUD variable, select All from the dropdown.
- Select a Service: Select the entity from the drop-down which lists the services available in your application.
- Variable Creation: Once you select the service and table/Entity for the service, a default variable will be created. See the Variable Name field populated by default which will be holding the dataset of the service. You can change the Variable name.
- Select Form As Dialog or Form Below, and Click Next.
- Select pagination, click Next.
- Configure table columns. These fields can also be configured using Advanced Settings from the Properties panel.
- Select template.
- Configure Form fields. These fields can also be configured using Advanced Settings from the Properties panel.
- Click Done.
For more information to create Datatable, see Create a Datatable.
Variable Properties and Events

You will be directed to the Variables page, with the new variable listed. You can see the following options.
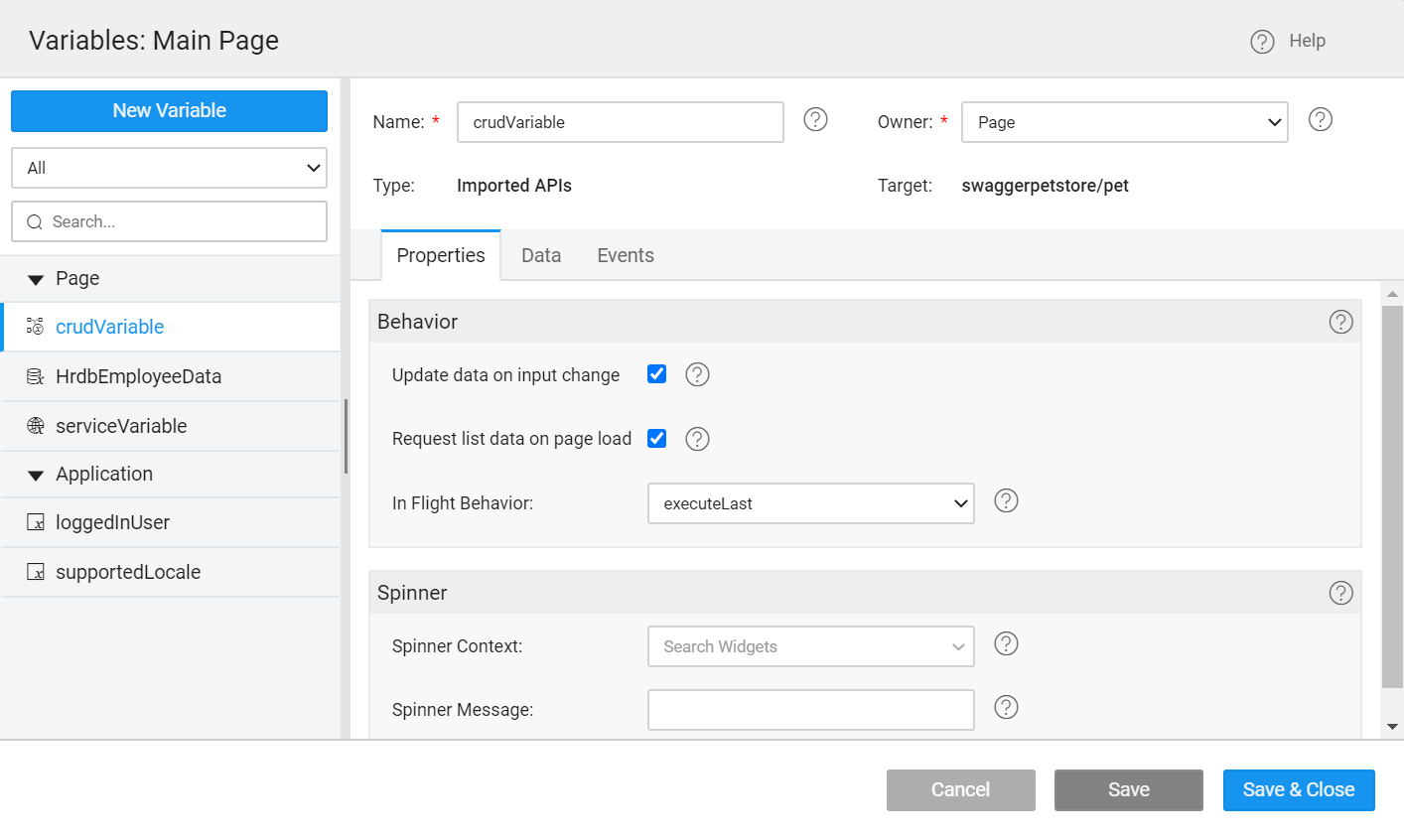
- Name: You can modify the variable name.
- Owner: The scope of the Variable. Page is the default option. You can choose Application to make it available across the app.
- A new Imported APIs Variable created with the default exposed method/selected method as a target.
- The Properties tab contains all the properties like behavior and spinner behavior. Learn more.
- The Data tab contains the fields serving as Input Fields for the API.
- The Events tab contains the events that can be configured to trigger any action. Learn more.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Behavior | |
| Update data on input change | If checked, the component will be triggered automatically on the change of input data (as mentioned in the data tab) for the variable. |
| Request data on page load | If checked, 'Page' variable will be triggered on page load while 'Application' variable will be triggered on application load. |
| In Flight Behavior | This property determines the behavior when a call is fired through the variable with the previous call still pending. Variable queues all these calls, waits for the previous call completion and then based on the value of the inFlightBehavior property, decides what to do with all the queued calls: - doNotExecute - all the queued calls will be discarded, - executeAll - all the calls will be triggered one by one, or - executeLast - only the last call is triggered and the rest are discarded, this is the default behavior |
| Spinner | |
| Spinner Context | This property specifies on which UI widget the spinner should show. Leave empty if no spinner required. |
| Spinner Message | The message to be displayed below the spinner. Leave empty if no message is required below the spinner. Note: If multiple variables are fired then the spinner messages will be displayed as a list below a single spinner. |
Events
During the life cycle of a Variable, a set of events are emitted by the Variable, thus giving you the option to control the behavior of the Variable such as input data validations, data processing, success/error handling, and more.
- OnBeforeUpdate
- OnResult
- OnError
- OnBeforeDatasetReady
- OnCanUpdate
- OnSuccess
To learn how to implement Events, see Events Documentation.
Methods
Few Methods are exposed for Variables which can be used for achieving more control and accessing extra functionality. Listed here are the same.
invoke()
This method updates the Variable’s dataSet with new data by making a call to the target service. There are four ways to call this method.
list.invoke()
create.invoke()
update.invoke()
delete.invoke()
Parameters
options (object) - It can have fields as:
inputFields(key-value pair of inputData)- success (callback)
- error (callback)
Return Value
none
Example
setInput(key, value)
This method sets the input field value against the specified field(key) for the specified operation(list, create, update or delete) based on how we call it. There are four ways to call a setInput method.
list.setInput(key, value)
create.setInput(key, value)
update.setInput(key, value)
delete.setInput(key, value)
Parameters
- key(string): name of the input field
- value(*): value for the input field
Return Value
- Updated
inputFieldsobject
Example
setInput(object)
This method can also be used to set all the specified key-value pairs as input fields in the variable for a particular operation(list, create, update or delete) based on how we call it. There are four ways to call a setInput method.
list.setInput(object)
create.setInput(object)
update.setInput(object)
delete.setInput(object)
Parameters
- Object: key-value pairs {“key”: “value”,…}
Return Value
- Updated
inputFieldsobject