App Security
The WaveMaker security feature offers comprehensive security solutions to secure the apps you develop. WaveMaker offers application level security and the two major areas including “Authentication” and “Authorization”.
Authentication
“Authentication” is the process of establishing a principal who they claim to be (a “principal” generally means a user, device or some other system which can perform an action in your application).
Authorization
“Authorization” or “Access-Control” refers to the process of deciding whether a principal is allowed to perform an action within your application.
Onboarding
"Onboarding" is the process of retrieving user's data from various providers like DB, LDAP, AD or any custom provider. This data includes roles and role groups information. Then, Authentication is done based on user credentials, which are obtained from the security provider; and Authorization or access to various app resources such as widgets, pages, data, and APIs can be controlled through configuration.
In WaveMaker, Security can be configured by selecting the Security option from the Project Configurations bar in the Project Workspace.
How App Security Works
Browser executed JavaScript can be easily manipulated. Therefore, security is server-side responsibility. WaveMaker server security consists of a series of filters. These filters determine if the request should be allowed. WaveMaker supports the following types of authentication:
- HTTP BASIC authentication headers - an IETF RFC-based standard
- LDAP/ AD - a very common approach to cross-platform authentication needs, especially in large environments
- Form-based authentication for simple user interface needs
- Automatic "remember-me" authentication
- Anonymous authentication allowing every unauthenticated call to automatically assume a particular security identity
If the server fails to authenticate a user, it will result in HTTP 401 response to the client. An authorization failure will result in 403 response sent to the client. If the requester is not logged in but must be, to access the requested resource, the user is redirected to the login page or can be prompted with a login dialog. If the user is logged in but lacks the credentials to access the requested resource, the request will be denied (403).
When security/authentication is enabled, all services are restricted to logged-in users by default. Only the login service is available to anonymous users. This can be customized using setup services.
WaveMaker also provides Role-based Access Control to control widget visibility. Role-based Access Control is a client-side function. As such, it should only be considered as a helper. It helps present the proper interface, based on the user's role. Role widget visibility must not be relied upon for securing resources. Take the example where only admin users are allowed to access a function invoked by a button click. Hiding the button to all but admin users via the client roles mechanism prevents non-admin users from expecting the button to work. However, the function of the button must be secured using server-side access control in order to be secure.
How security is implemented
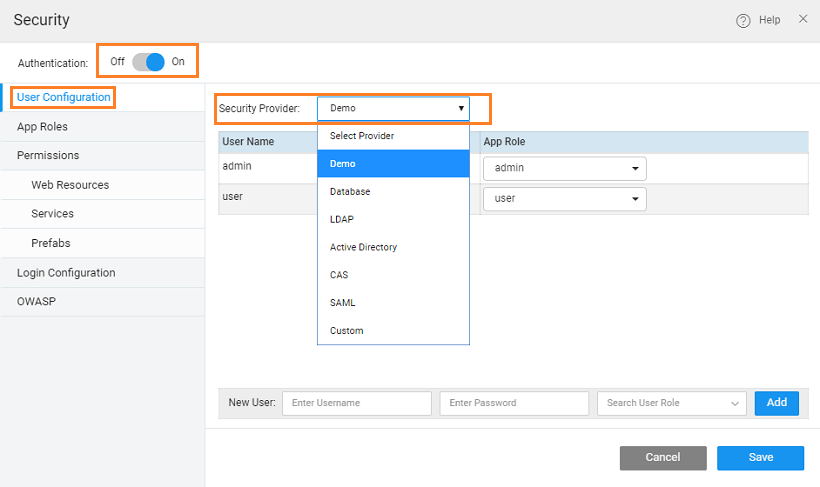
Once Authentication is switched on the User Configuration information can be obtained from Service Providers like Database, LDAP, AD or any custom provider.
Depending on the security provider enabled, users and roles are on-boarded through configuration. Details regarding the access to details and the corresponding App role needs to be configured.
App Roles
App Roles need to be added based on the configuration. By default, the platform provides with two roles admin and user. You can either retain/delete the same and further add to the list. When adding new App Roles ensure that the Roles are specified by the selected service provider.
Permissions
Permissions can be set to app resources such as pages and services i.e. database, API & custom Java using the above-configured app roles. Accessibility or the level of visibility for each UI component can be configured separately from the widget properties. Widgets can be made accessible to certain roles or role groups based on the configuration.
Login
Application Login can be configured using a Page or a Dialog. Each role defined in the application can have a separate landing page.
OWASP
Security vulnerabilities like XSS and CSRF can be prevented from the OWASP Configuration.
Security Terminology
The various terminology used by WaveMaker concerning Security:
- Authentication: a process by which the access to app restricted to known/authentic users.
- Authorization: a process by which the access to various aspects of the app such as services, widgets, and functionality; is restricted to the specified app roles.
- Users: Authentic users of the app identified via a Username and Password.
- App Roles identify the level of authorization allowed to a given user. These roles are assigned to Users mentioned in the previous step.
- Permissions: Each of the web resource and service used in an app is assigned various permission levels:
- Everyone - anyone can access this item i.e. no authentication required
- Authenticated - these items are accessible to authenticated users who will be identified via the roles assigned to them
- Anonymous - widgets at this access level are visible to only users who are not logged in. _
This setting can be used only for widget access.
The permission levels follow a hierarchical structure with child element inheriting parent permissions if none are specified.
- Login Configuration defines the login behavior once authentication is enabled. There are two behaviors that can be defined - login page and landing page:
- specify the UI for login - dialog or page. In the case of a page for login, you can use the default login page provided by Studio or design your own login page.
- Landing Page defines the page to be displayed once the user logs in. The page to be displayed can be defined based upon the role of the logged in user.