Creating Form
The Form widget has inbuilt functionality to perform POST & GET operations on the data source it is bound to. A typical Form set up in WaveMaker has the following steps:
- Set the data source that the Form will be working on. This takes the form of a variable based on the APIs exposed by Java Service Integration or Web Service Integration.
- Select the display layout of the Form. You can choose from one-column, two-column or a three-column layout.
- Select the fields to be available for the user to interact with. All the fields from the selected data source will be presented for selection and assign the display widget for each.
Drag and drop the Form widget onto the page.
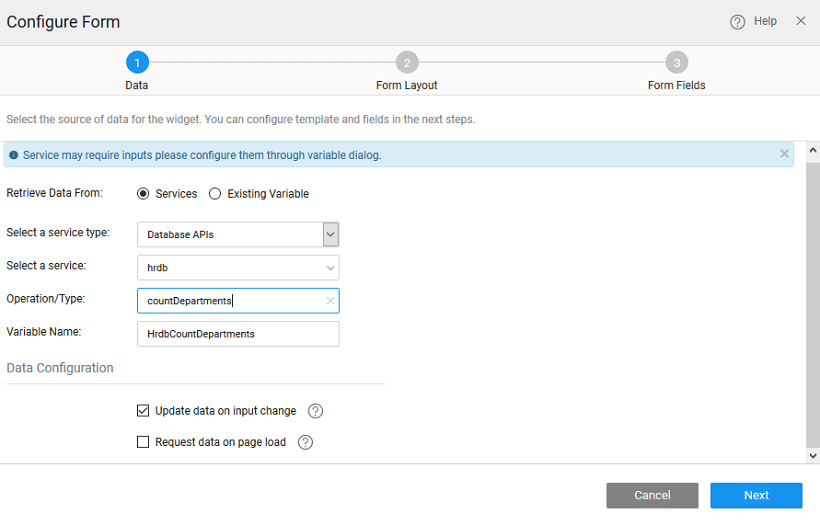
STEP 1 – Select Data
There can be different scenarios to deal with when configuring your Form Widget with a data source. The data source can be in the form of a variable based on the APIs exposed by the imported web, java or query service.
Scenario 1
You do not have any services available in your project. In this scenario, no variables can be created as there are no services available in your project.
- You will be prompted to import either a database or web service or create a java service. Click the appropriate button to proceed.
- Once a service is available in your application, you can proceed to bind the widget to data source and follow the same steps as mentioned in scenario 2.
Scenario 2
There are no variables created for any of the services in your application
- Retrieve Data From: Services is selected by default. If no widgets are placed in the current page, the widgets option will be disabled.
- Select the Services option.
- Select a Service: Select a service from the drop-down which lists the services available in your application.
- Select the Table/Entity of the service which would correspond to the functions, methods or queries for DB services respectively.
- Variable Creation: Once you select the service and Table/Entity for the service, a default variable will be created for you – see the Variable Name field populated by default which will be holding the dataset of the service. You can also change the Variable name.
- Data Configuration Options: You can also set the following Data Configuration options:
- Update Data on input change: which is checked on by default. This means that whenever there is a change in the input parameter or filter field of the variable the data will be fetched from the service. This option will have an impact on the app performance.
- Request data on Page Load: which is checked on by default. This allows for data to be shown when the page is loaded. If this is not checked, you will not be able to view the data when the page gets loaded. Instead, No Data Found message appears on the widget at runtime.
Scenario 3
If the database API variables are already created in the project
- Retrieve Data From: Services, Existing Variables or Widgets are the options provided to you for choosing the source of data.
- Select Existing Variable. Note that you can create a new variable if required.
- Select a Variable from the drop-down list of the variables available in the application. You can select the one needed to bind the List Widget to. You can also search for a specific variable by typing in select variable option. If you are able to find your variable in the drop-down select the same.
- Once you select the variables, it shows the dataset that it is bound to.
- As Data Configuration options are already set for this variable, you do not see those options in this scenario.
STEP 2: Layout and Alignment Configuration
- You can choose to have a 1, 2 or 3-column layout.
- You can set the Alignment, Position, and Size of the Caption for the Form.
STEP 3: Field Configuration
- The View As widget to represent the selected field. The widgets applicable to the field based on the field data type, are available for selection from the drop-down box.
- In the case of a multi-column layout, you can choose the fields to be displayed in the respective columns. You can use the up and down arrows to arrange the fields.
Using Form to trigger an Insert Query
We will be seeing how to use a Form to insert values into an Employee table of the hrdb database using Insert Query:
- Create a query in database designer with input params
- Provide test values and run and save the query (as InsertEmp).
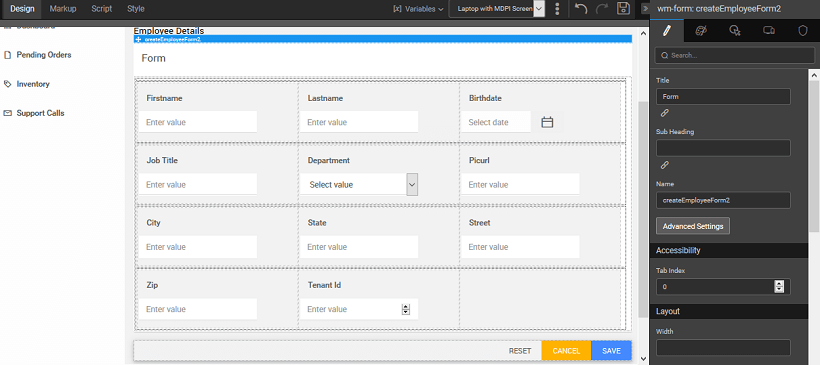
- Create a variable by dragging and dropping Form widget and using Create new functionality or by using this query operation from the variable dialog.
- Select Layout and Configure Fields changing the display name and widget type if needed. Note that if the database API Variable underlying the Form, has to have some input fields the same should be done using the Data tab of the Variable.
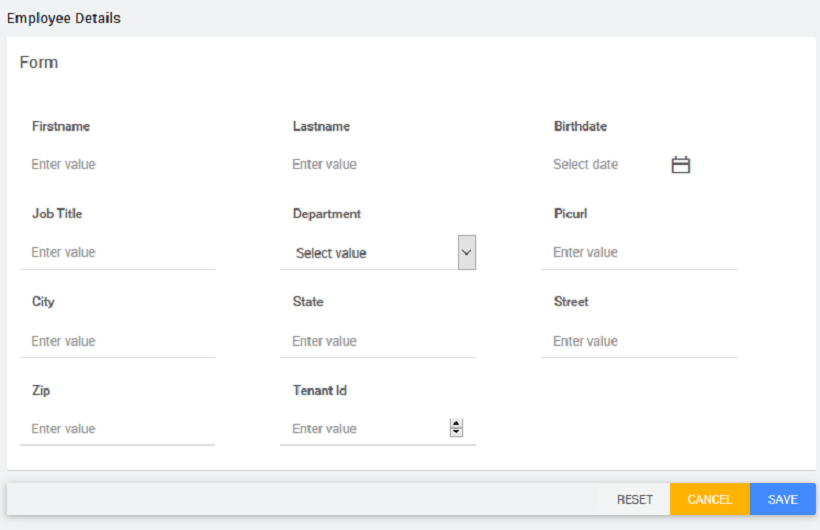
- Your page will look like this in design mode.
- Run the app, enter the values and SAVE.
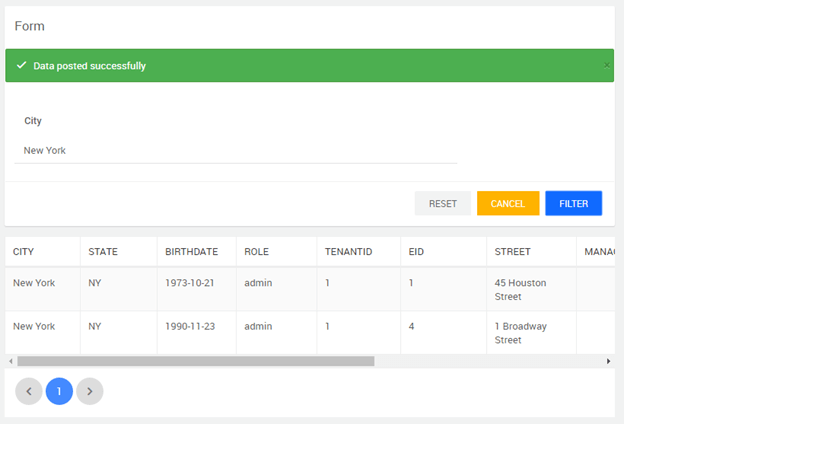
Using Form as Filter
A form can be used as a filter for GET type of API’s.
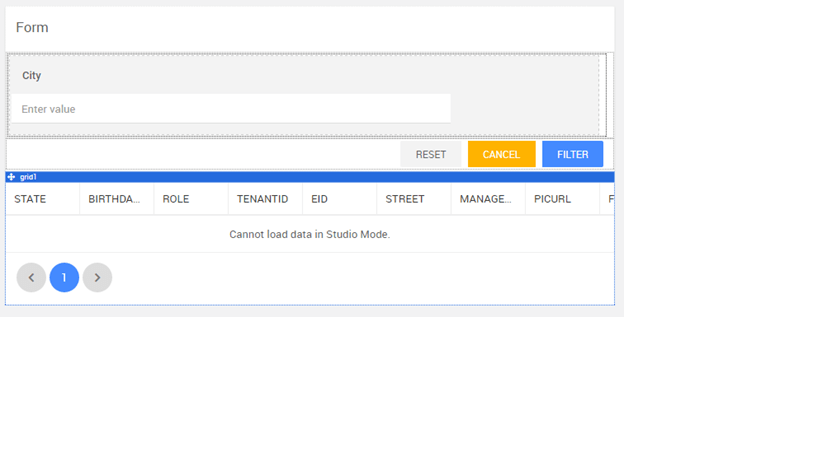
Below example is for filtering the data using a query. We will be using the Employee table of the hrdb database to filter on city field.
- Create a query in database designer with input params.
- Provide test values and run and save the query (as EmpByCity).
- Create a variable using this query operation from the variable dialog or dragging and dropping Form widget and using Create new functionality.
- Select Layout and Configure Fields changing the display name and widget type if needed.
- Drag and drop a Data Table onto the canvas and bind it to the Database API Variable created when configuring Form. Your page will look like this in design mode.
We have changed the name of the SAVE button to FILTER
- Run the app, enter the values and FILTER, see the content of the Data Table change.