Pre-Post Processing for Database Service APIs
The following procedure specified in this document will no longer work. We recommend you follow Database CRUD Operations Event Listeners instead.
Introduction
This document will go through the steps in adding pre and post-processing for generated APIs in an imported Database service.
Pre-requisites
- Create a WaveMaker Project (UserManagementApp)
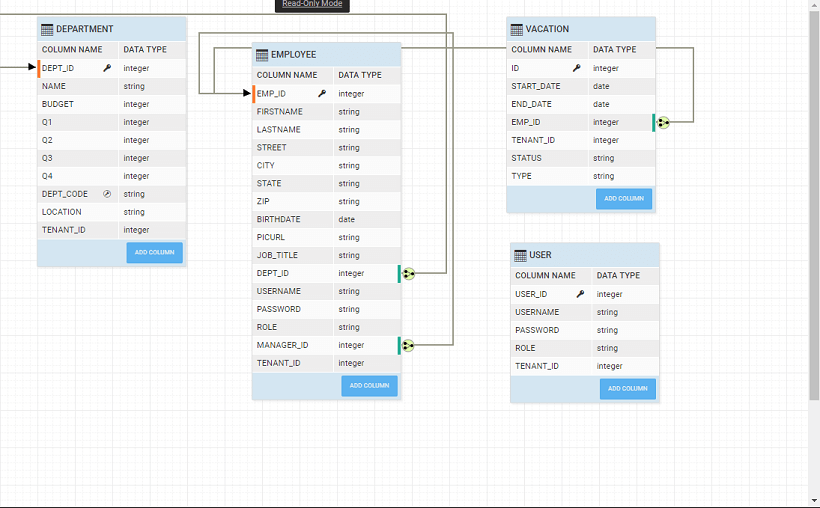
- Import a database service: (we are using the sample HRDB)
- Set Security to On. Use Database as Security Provider and Configure Security with user table of HRDB.
Background
When a database is imported into a WaveMaker app, Java code with Spring based REST APIs for all CRUD operations on each database entity are generated. Generated APIs include endpoints to search(filter), get count of and export data. WaveMaker also understands the relations across the tables and generates the associated APIs as well.
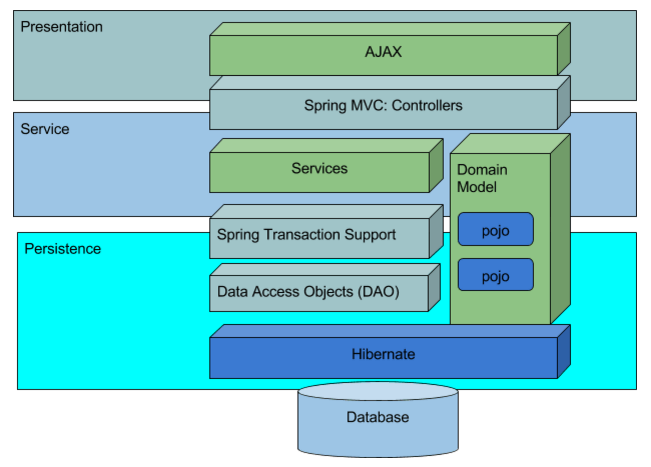
There are 3 layers in the generated source code:
- Layer 1 : REST Controller responsible for transporting the data between client and server, authorization of APIs & marshalling and unmarshalling of model to JSON etc.
- Layer 2: Service Layer - responsible for validating the inputs and transaction management
- Layer 3: DAO Layer - responsible for interacting with the underlying database. This code uses Hibernate framework.
The diagram below depicts the Layered Architecture mentioned above:
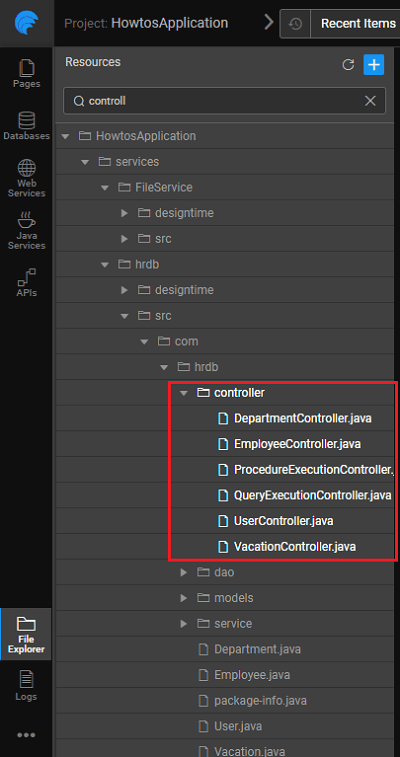
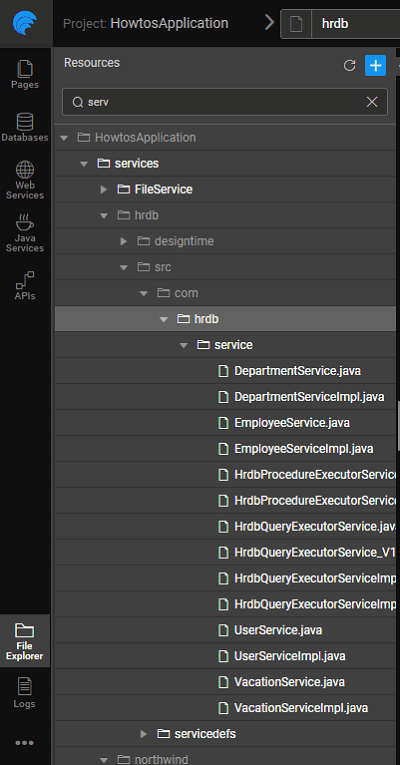
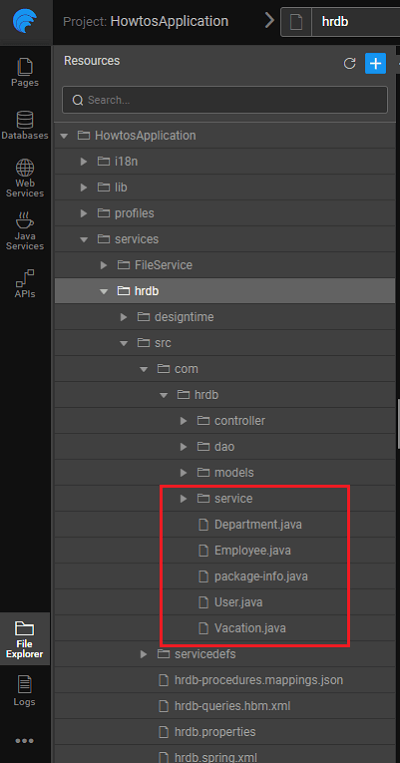
The screenshots below show the folder structure of the generated code.
- Controllers are generated for entities, queries and procedures
- Data Access Objects (DAO) for each of the entities
- Service Interfaces and Service Implementations for entities, queries and procedures
- POJOs for each entity
Each of the layers performs its responsibilities and delegates the call to the next layer in the chain. For example, after the unmarshaling of the JSON data to model, and authorization checks, the REST layer delegates the call to the service layer etc.
Pre-Post Processing
Since the code gets generated every time any Database operation like Re-Import or Update, etc. are performed, any custom code within the generated code will be overwritten. Hence, we will create a new Java class to extend the service implementation class and override the required method.
The service layer is the entry point for writing custom/pre-post processing for any additional business logic when an API is invoked from the browser/UI.
The service layer itself is provided with a Java interface & default implementation generated.
To write a pre-post processing of service implement the following steps.
Step 1: Service implementation class
Write a new service implementation class by extending the existing Service Impl
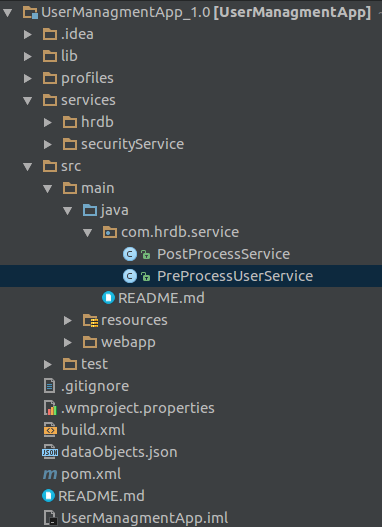
- Create a service in user src/main/java folder of the project Example: UserManagementApp/src/main/java/com/hrdb/service/PreProcessUserService.java
Please refer the documentation to add the files in project.
Step 2: Extend service impl class and override method
Extend the UserServiceImpl to preprocess the service.
You can Override only those methods which need extra processing in one of the following ways
- Delegate after the pre-processing to the superclass
- Or invoke directly the DAO layer
- Or throw exceptions it appropriate
- You can also inject multiple other services into this new class & perform multiple actions in it, say inject SecurityService & perform additional security checks etc.
In this example we have implemented the first way, i.e. delegate to superclass. A service is written to check if the login user is an admin and if the user is admin then the user details are fetched. Find below the code for both PreProcessService and PostProcessService classes Note : Please create these classes in an IDE and copy it in path specified in the following screenshot, see here to know how to work with IDE.
**`PreProcessUserService.java
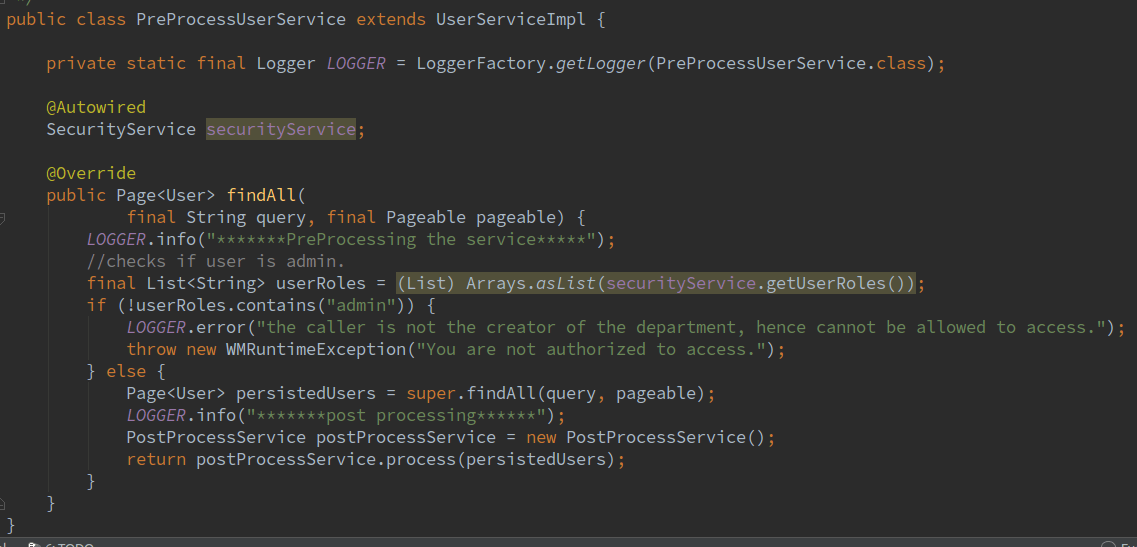
PostProcessService.java Imports:
Step 3: Override the bean class
- Let the REST layer use your implementation rather than using the default service impl by overriding the bean-class in the user-spring xml.
- Now in
project-user-spring.xmladd the bean to declare the Service which user has defined.
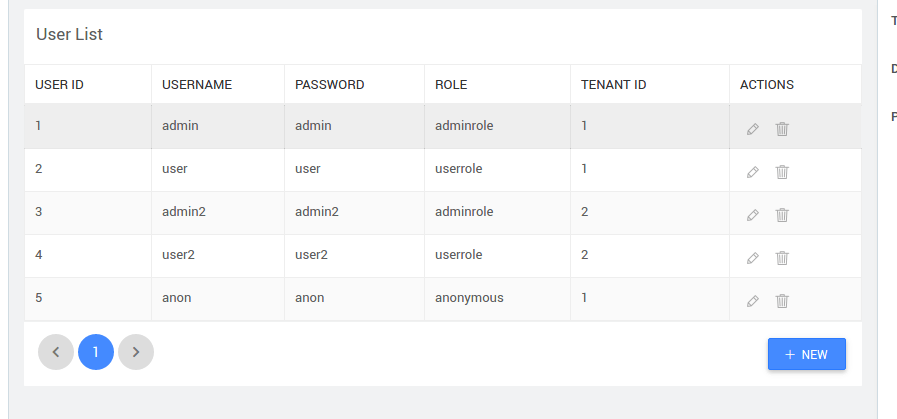
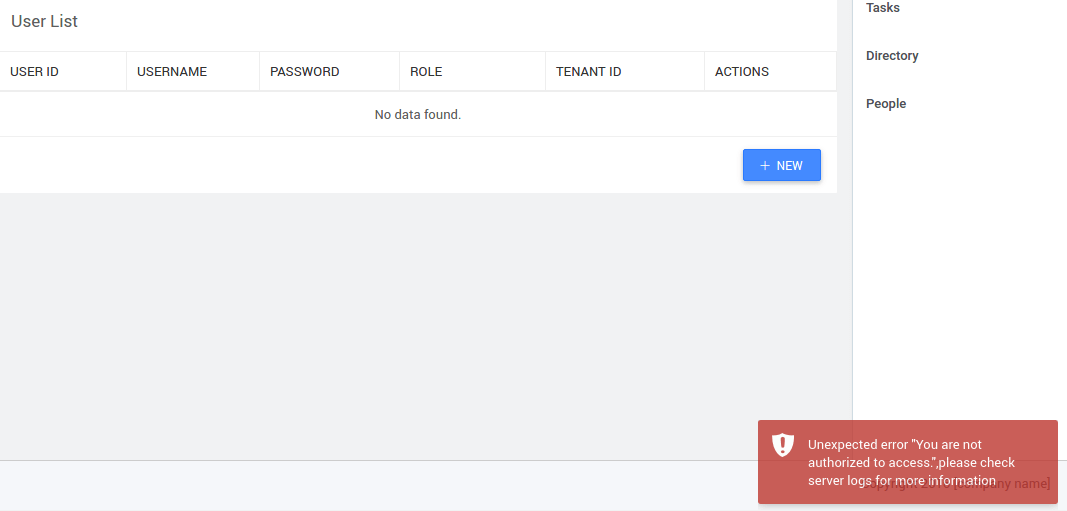
At run-time, data is fetched for admin.
For other users, an error is thrown as shown below.
See Also
How to send emails using Java Service
How to implement forgot password feature using Java Service
How to access REST APIs from Java Service
How to schedule a Java Service