Single Page App
A Single Page App (SPA) significantly enhances how the application UI renders by providing a more seamless and responsive user experience. Instead of loading entire pages from the server with each user interaction, an SPA dynamically updates the content within the existing page, loading all necessary resources upfront.
What Happens with SPA Behavior
Enabling SPA behavior ensures that navigation across pages only updates the content section, while static areas such as the header, left navigation, and footer remain unchanged. This results in smoother page transitions.
With release 11.8.0, SPA behavior will be enabled in the new applications by default. You need to enable it for the previously created applications.
How SPA Works
Once the SPA behaviour is enabled,
- Page entirely loads when the layout is different which includes the static areas like, header, leftnav, footer and the partials used in the page.
- Only the page content loads when both the overall layout and the included partials remain the same.
How SPA Helps with User Experience
- Faster Load Times: Provides quicker load times and smoother transitions between pages.
- Reduced Server Load: Reduces server load by only loading data as needed and making fewer requests.
SPA will only function for deployed apps. There is no SPA for preview as of now.
Enabling SPA Behavior
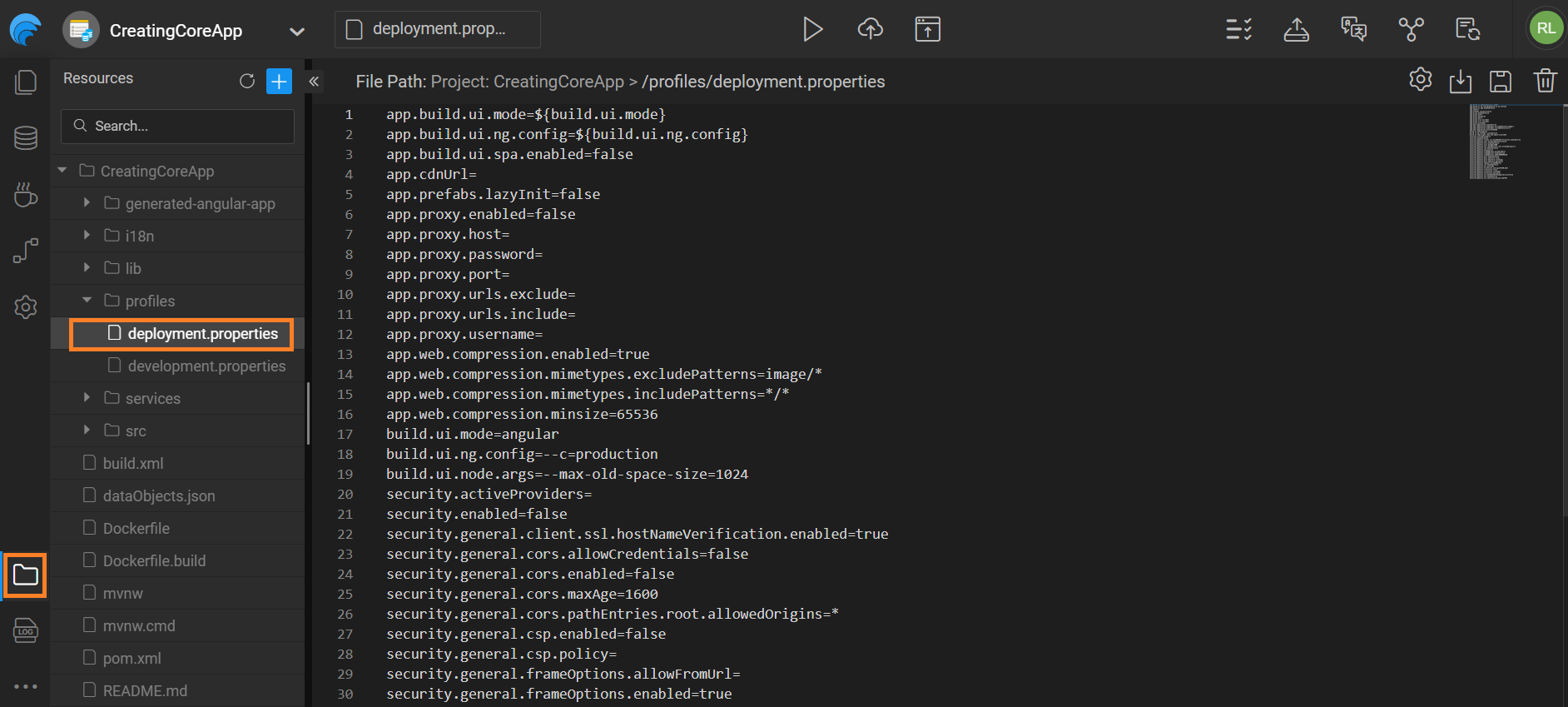
To enable SPA behavior, set the SPA flag to True in the File Explorer. This flag is set to False by default.
- Go to File Explorer. Go to Project path -> Profiles -> Deployment Properties.
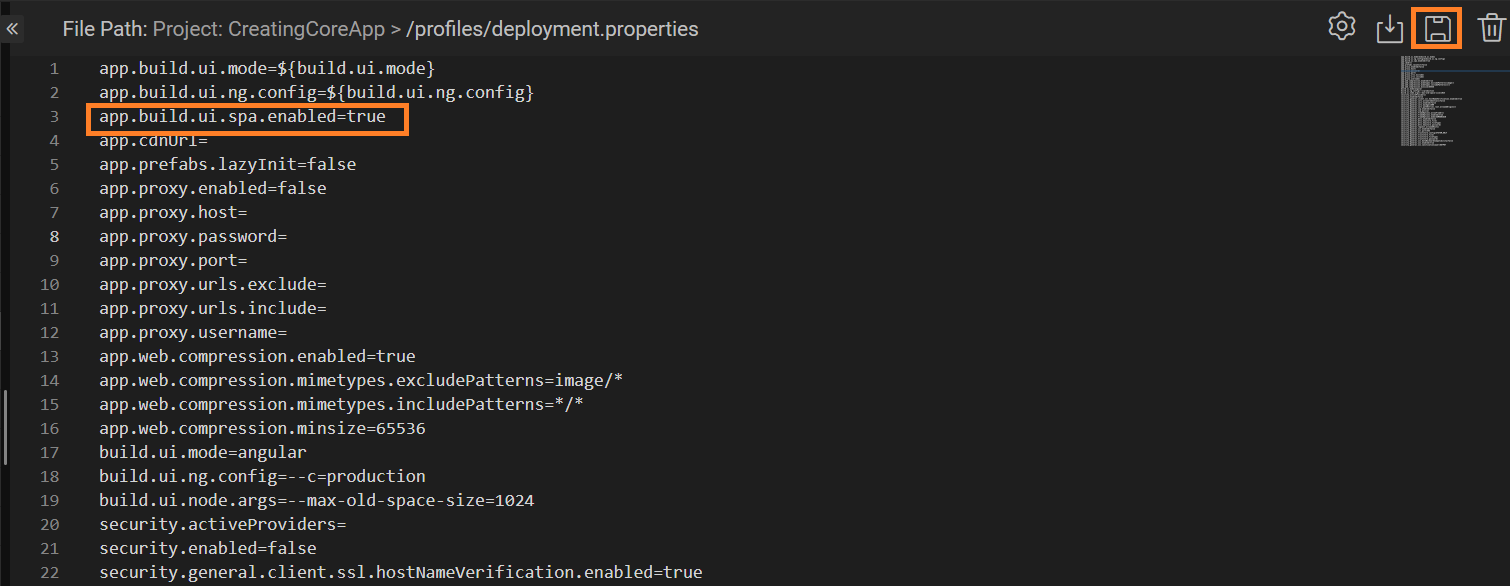
- Set the flag to
trueby adding the below code and click Save.
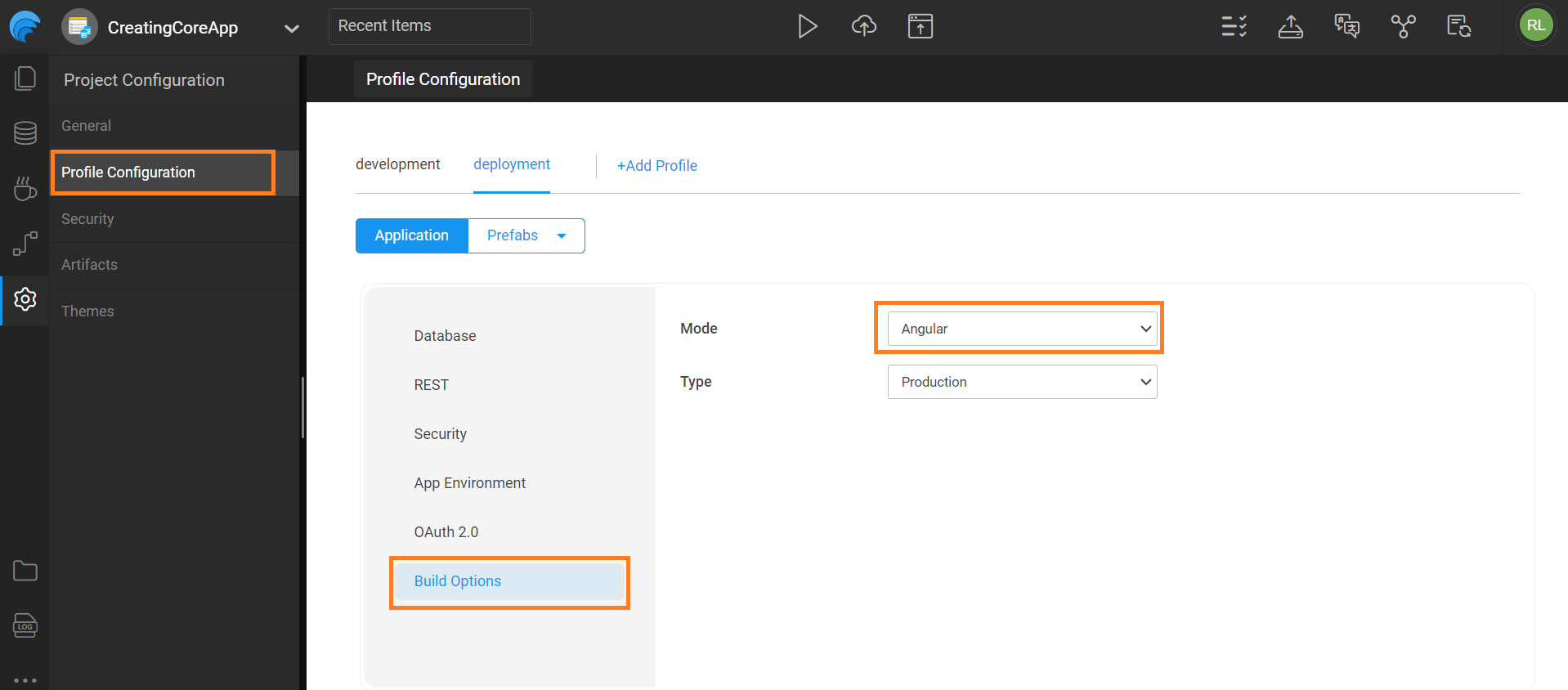
- Next, go to Settings > Profile Configuration. Switch to deployment and navigate to Build Options to set the build mode to Angular.
It is recommended to set the build mode as Angular. This allows you to use the Angular package for deployment.
- Now deploy the application and see how the app renders after enabling SPA behavior.
Scenarios to Check
After enabling the SPA behavior, it is recommended to check a few scenarios to confirm successful implementation.
- If the content in header, topnav, leftnav, and rightnav is rendered dynamically. For example, content is bound to an API variable.
- If the content is changed dynamically through
Partial.onReadyevent for the partials and show/hide attributes of the components in the partials depend on JavaScript expressions.