Single Sign-On Across Mobile Apps Using OAuth 2.0 with PKCE
OAuth 2.0 with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) provides a secure authentication mechanism for mobile applications. This documentation covers implementing Silent Single Sign-On (SSO) functionality, allowing users to authenticate once and seamlessly access multiple applications without repeated login prompts.
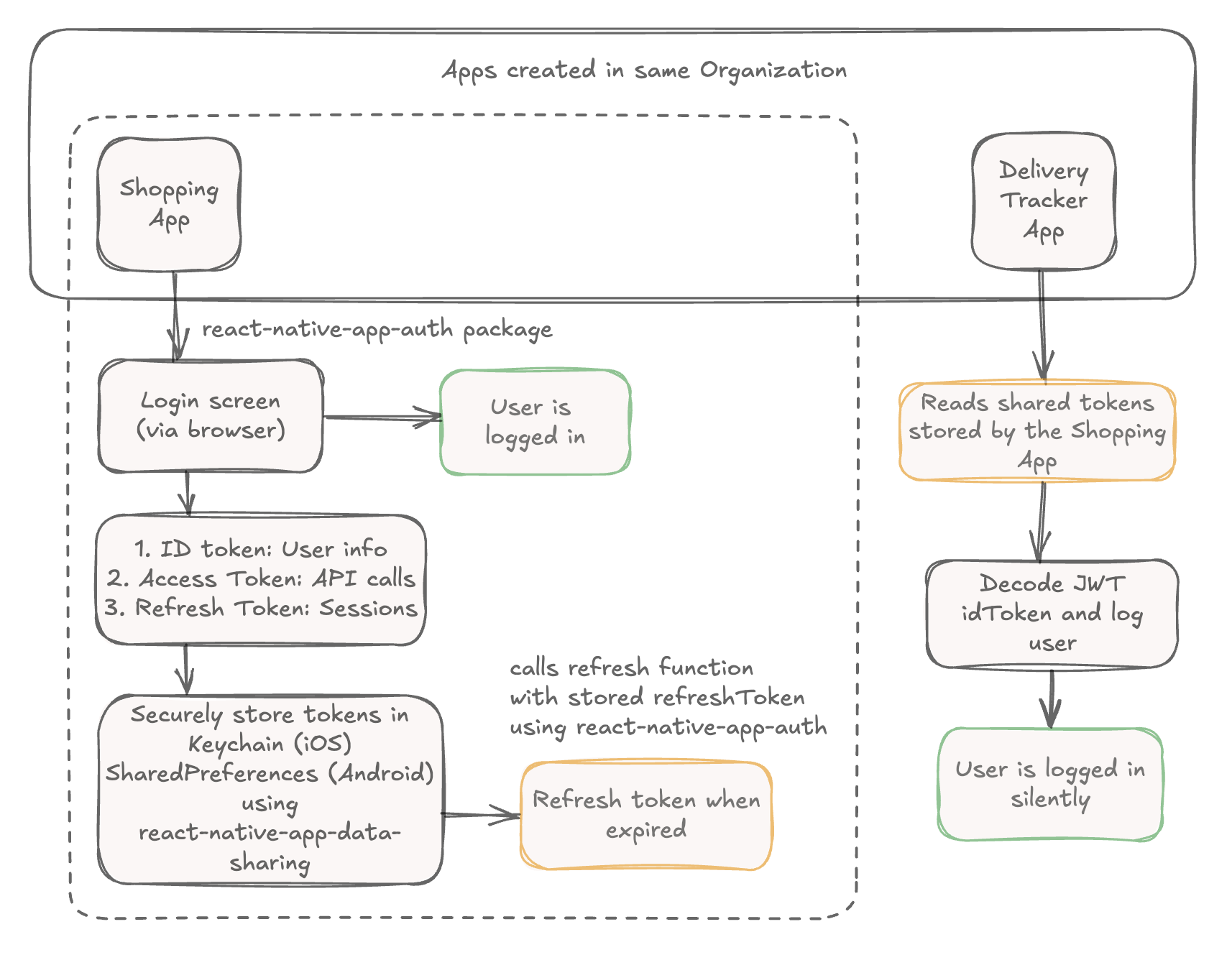
For example, imagine an organization that offers a suite of mobile apps, such as a shopping app, a delivery app, and a loyalty app. With Silent SSO, users can log in to one app (e.g., the shopping app), and then switch to the other apps without needing to log in again. This improves user experience while maintaining strong security.
Here, the implementation uses OAuth 2.0 with PKCE extension, which adds an extra layer of security specifically designed for public clients like mobile applications.
This Allows
- Enhanced User Experience: Users authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications
- Improved Security: PKCE prevents authorization code interception attacks
- Token Management: Automatic token refresh maintains user sessions seamlessly
- Cross-App Authentication: Secure token sharing between applications
Prerequisites
To enable Silent Single Sign-On (SSO) across mobile applications using OAuth 2.0 with PKCE, you will need the following libraries:
Core Authentication Library
Library: react-native-app-auth
This provides OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect authentication capabilities, such as PKCE flow support out-of-the-box, and handles token management.
Installation:
npm install react-native-app-auth
Data Sharing library
Library: react-native-app-data-sharing
This enables secure data sharing between applications on both iOS and Android, and provides unified API for Keychain (iOS) and SharedPreferences (Android).
npm install react-native-app-data-sharing
Standard packages like expo-secure-store cannot be used for cross-app data sharing as each application has sandboxed storage that cannot be accessed by other applications.
Secure Token Sharing
To achieve silent SSO across applications, authentication tokens must be securely shared between apps. The recommended approach involves:
iOS Implementation:
- Use App Groups and Keychain services to share data between applications
- Keychain provides encrypted storage that can be accessed by multiple apps within the same App Group
Android Implementation:
- Utilize SharedPreferences API with appropriate security configurations
- Enable data sharing between applications with the same signature
JWT Token Decoding
Since the stored ID token is a JWT (JSON Web Token), it can be decoded to extract user information when logging into subsequent applications. This eliminates the need for additional API calls to retrieve user data.
Expo Plugin Integration
For projects using Expo's managed workflow, native code modifications are handled through plugins rather than manual configuration.
Required Expo Plugins
@wavemaker/react-native-app-auth-expo-plugin
- Configures native changes for OAuth authentication
@wavemaker/react-native-app-data-sharing-expo-plugin
- Sets up App Groups (iOS) and SharedPreferences (Android) configuration
Plugin Setup Process
Install the required libraries and expo plugins:
npm install react-native-app-auth react-native-app-data-sharing jwt-decode
npm install @wavemaker/react-native-app-auth-expo-plugin
npm install @wavemaker/react-native-app-data-sharing-expo-plugin
Configure both plugins in your app.json or app.config.js:
{
"expo": {
"ios": {
"bundleIdentifier": "com.yourcompany.app1",
"entitlements": {
"com.apple.security.application-groups": [
"group.com.yourcompany.sso"
],
"keychain-access-groups": [
"$(TeamIdentifierPrefix)group.com.yourcompany.sso"
]
}
},
"plugins": [
[
"@wavemaker/react-native-app-auth-expo-plugin",
{
"redirectScheme": "com.org.myapp.auth",
"enableUniversalLinks": false
}
],
[
"@wavemaker/react-native-app-data-sharing-expo-plugin",
{
"appsBundleIds": ["com.yourcompany.app2", "com.yourcompany.app3"]
}
]
]
}
}
Generate native code: npx expo prebuild --clean
Run development build: npx expo run:android or npx expo run:ios
This managed workflow allows us to benefit from Expo's Continuous Native Generation (CNG) while incorporating necessary native modifications through plugins.
Login flow
Initial Authentication in App 1
The first application in your SSO ecosystem performs the complete OAuth 2.0 authentication flow and securely stores the resulting tokens for other applications to access. This establishes the foundation for silent login across multiple apps within your organization.
import { authorize, refresh } from 'react-native-app-auth';
import { saveData, getData, initializeStore } from 'react-native-app-data-sharing';
import { jwtDecode } from 'jwt-decode';
const authConfig = {
issuer: 'https://accounts.google.com',
clientId: 'your-client-id.apps.googleusercontent.com',
redirectUrl: 'com.org.myapp.auth://oauth/redirect',
scopes: ['openid', 'profile', 'email', 'offline_access'],
usePKCE: true,
useNonce: true,
additionalParameters: {},
};
export const performInitialLogin = async () => {
try {
console.log('Starting OAuth 2.0 authentication...');
initializeDataSharing();
const result = await authorize(authConfig);
console.log('Authentication successful:', {
accessToken: result.accessToken ? 'Present' : 'Missing',
refreshToken: result.refreshToken ? 'Present' : 'Missing',
expirationDate: result.accessTokenExpirationDate
});
await storeTokensSecurely(result);
const userInfo = decodeJWTToken(result.idToken);
if (userInfo) {
await storeUserInfo(userInfo);
}
return {
success: true,
tokens: result,
user: userInfo
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Authentication error:', error);
}
};
const decodeJWTToken = (idToken) => {
if (!idToken) {
console.warn('No ID token provided for decoding');
return null;
}
try {
const payload = jwtDecode(idToken);
console.log('JWT decoded successfully:', {
sub: payload.sub,
email: payload.email,
name: payload.name
});
return payload;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error decoding JWT token:', error);
return null;
}
};
Token Storage
After successful initial authentication, the application securely stores:
- Access Token: Short-lived token for API authentication
- Refresh Token: Long-lived token for obtaining new access tokens
- Expiration Data: Access token expiry timestamp for proactive refresh
import { saveData, getData, initializeStore, getAllSyncData } from 'react-native-app-data-sharing';
const initializeDataSharing = () => {
initializeStore({
android: {
appsBundleIds: ['com.yourcompany.app2', 'com.yourcompany.app3']
},
ios: {
accessGroup: 'group.com.yourcompany.sso',
serviceName: 'com.yourcompany.sso',
},
});
};
const storeTokensSecurely = async (authResult) => {
try {
const tokenData = {
accessToken: authResult.accessToken,
refreshToken: authResult.refreshToken,
expirationDate: authResult.accessTokenExpirationDate,
tokenType: authResult.tokenType || 'Bearer',
scopes: authResult.scopes,
idToken: authResult.idToken,
timestamp: Date.now()
};
await saveData('oauth_tokens', JSON.stringify(tokenData));
console.log('Tokens stored successfully for SSO');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error storing tokens:', error);
}
};
const storeUserInfo = async (userInfo) => {
try {
const userData = {
userId: userInfo.sub,
email: userInfo.email,
name: userInfo.name,
picture: userInfo.picture,
givenName: userInfo.given_name,
familyName: userInfo.family_name,
};
await saveData('user_info', JSON.stringify(userData));
console.log('User info stored successfully');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error storing user info:', error);
}
};
Silent Login in App 2
Subsequent applications can authenticate users automatically by reading the shared tokens stored by App 1. This process checks for valid tokens, refreshes them if needed, and logs the user in seamlessly without requiring manual authentication.
import { saveData, getData, initializeStore } from 'react-native-app-data-sharing';
import { refresh } from 'react-native-app-auth';
export const silentLogin = async () => {
try {
console.log('Attempting silent login...');
initializeDataSharing();
const storedTokens = await getStoredTokens();
if (!storedTokens) {
console.log('No stored tokens found');
return { success: false, reason: 'NO_TOKENS' };
}
if (isTokenValid(storedTokens.accessToken, storedTokens.expirationDate)) {
console.log('Stored access token is still valid');
const userInfo = await getStoredUserInfo();
return {
success: true,
tokens: storedTokens,
user: userInfo,
source: 'STORED_TOKEN'
};
} else if (storedTokens.refreshToken) {
console.log('Access token expired, attempting refresh...');
const refreshedTokens = await refreshAccessToken(storedTokens.refreshToken);
if (refreshedTokens) {
await storeTokensSecurely(refreshedTokens);
const userInfo = await getStoredUserInfo();
console.log('Token refresh successful');
return {
success: true,
tokens: refreshedTokens,
user: userInfo,
source: 'REFRESHED_TOKEN'
};
}
}
console.log('All tokens are invalid or expired');
return { success: false, reason: 'TOKENS_EXPIRED' };
} catch (error) {
console.error('Silent login failed:', error);
return { success: false, reason: 'ERROR', error };
}
};
const refreshAccessToken = async (refreshToken) => {
try {
console.log('Refreshing access token...');
const refreshResult = await refresh(authConfig, {
refreshToken: refreshToken,
});
console.log('Token refresh successful:', {
accessToken: refreshResult.accessToken ? 'Present' : 'Missing',
expirationDate: refreshResult.accessTokenExpirationDate
});
return refreshResult;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Token refresh error:', error);
}
};
const getStoredTokens = async () => {
try {
const tokenString = await getData('oauth_tokens');
return tokenString ? JSON.parse(tokenString) : null;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error retrieving stored tokens:', error);
return null;
}
};
const getStoredUserInfo = async () => {
try {
const userString = await getData('user_info');
return userString ? JSON.parse(userString) : null;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error retrieving user info:', error);
return null;
}
};
const isTokenValid = (accessToken, expirationDate) => {
if (!accessToken || !expirationDate) return false;
const now = Date.now();
const expiry = new Date(expirationDate).getTime();
const bufferTime = 5 * 60 * 1000;
return expiry > (now + bufferTime);
};
const clearStoredTokens = async () => {
try {
await deleteData('oauth_tokens');
await deleteData('user_info');
console.log('Stored tokens cleared successfully');
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error clearing stored tokens:', error);
}
};
const getAllSharedData = async () => {
try {
const allData = await getAllSyncData();
console.log('All shared data:', allData);
return allData;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error retrieving all shared data:', error);
return null;
}
};
The silentLogin function can also be used in App 1 when the app is reopened or during app launch to check for existing valid tokens, avoiding the need for users to re-authenticate if they have previously logged in.
Refresh Token Flow
The refresh token mechanism ensures seamless user experience by automatically renewing expired access tokens without user intervention.
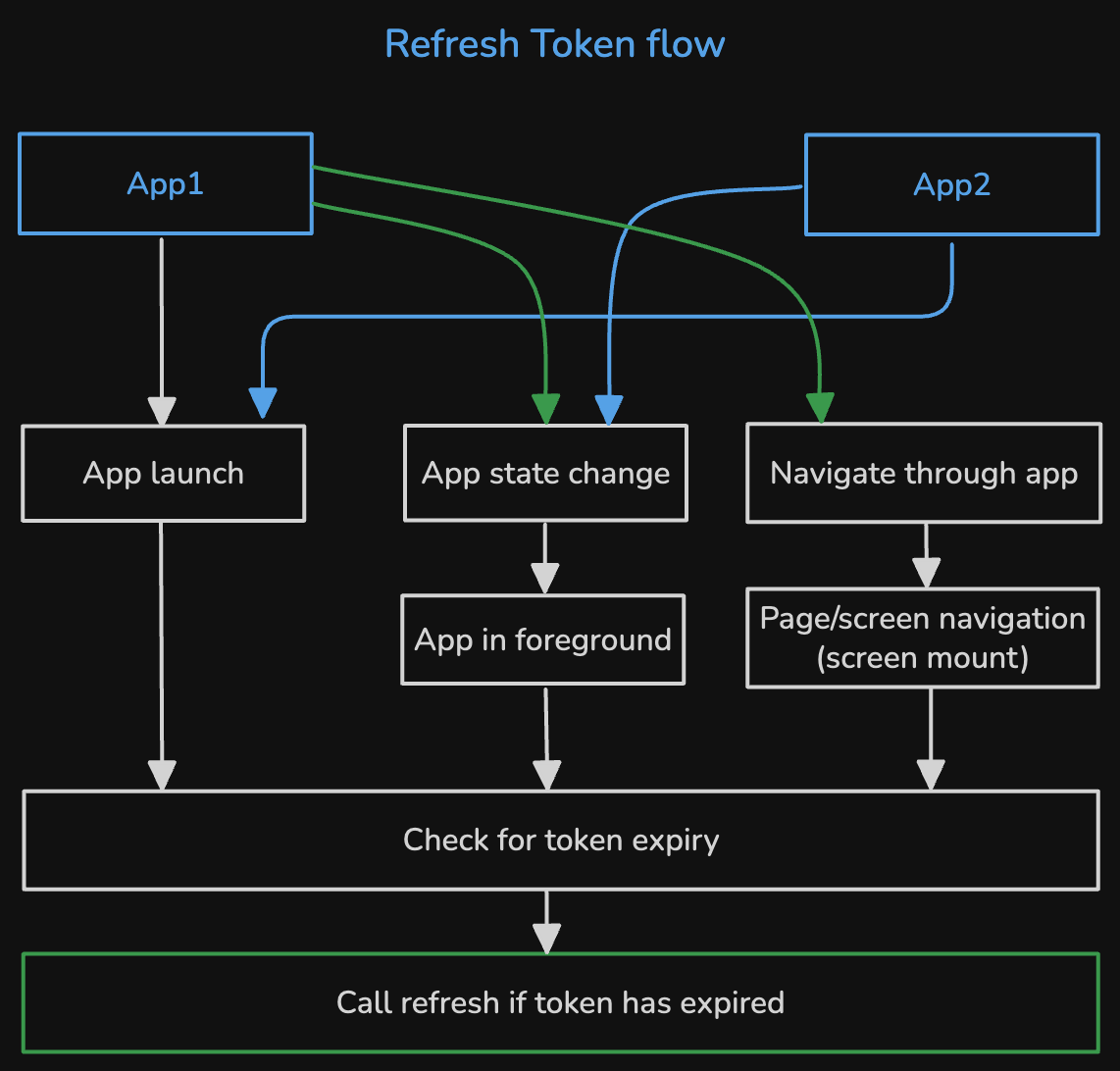
Automatic Token Refresh Triggers
The application monitors token expiration at strategic points:
1. Application Launch
Check token validity when the user opens the application
2. Application Foregrounding
Monitor app state changes using React Native's AppState listener to detect when the app transitions from background to foreground
3. Screen Navigation
Implement token validation during screen navigation (often implemented using a useFocusEffect hook from React Navigation).
Token Refresh Process
- Expiration Check: Verify if the current access token has expired
- Refresh Token Validation: Ensure a valid refresh token exists
- Token Refresh Call: Use the refresh token to obtain new access and refresh tokens
- State Update: Store the new tokens securely using the data sharing library
- Error Handling: If refresh fails, redirect user to login flow
References

