A case study on Certificate Pinning.
Introduction
In HTTPS handshake, the server responds with a public certificate issued by Certificate Authority (CA) to establish a connection. If CA, or Root certificate was compromised and issues a certificate without the domain owner's consent, the client may face the Man-in-the-middle (MTM) attack. To protect users from this vulnerability, an app can employ SSL pinning.
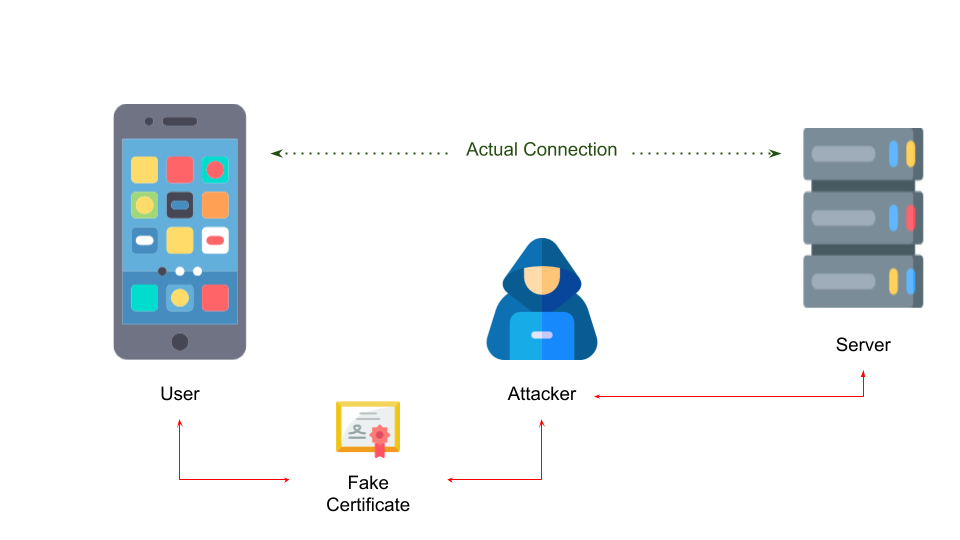
Certificate Pinning is an additional layer of security that protects communication between client and server. The Standard HTTPS verifies whether the connection is secure but it cannot verify whether you are communicating with the actual server or an intercepted server.
What Certificate Pinning offers
Standard HTTPS establishes a secure connection and checks whether the server certificate was issued by a trusted CA. Certificate Pinning additionally forces the client app to validate the server certificate with a known copy of the certificate.
The client application contains the pinned certificates which are pre-defined "known" certificates. During the time of communication between the client and server, the client expects the server certificate to match with any one of the pinned certificates. If it does not match, the client will terminate the connection.
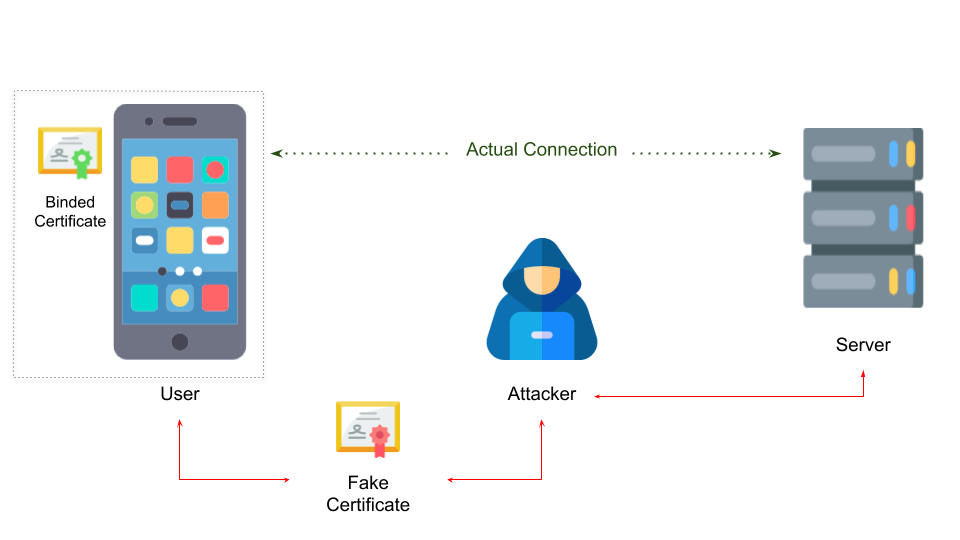
Web Certificate Pinning
Web Certificate Pinning is dynamic pinning. Certificates are pinned during the initial connection establishment. It was introduced in 2015 but was deprecated in 2018 due problems it created than resolving the actual problem.
Mobile Certificate Pinning
Mobile Certificate Pinning is static pinning, in which the certificate is bundled with the app. This means new app has to be installed on the certificate expiry.
Advantages of Certificate Pinning
- Certificate Pinning protects data tampering even if the user installs a malicious CA with or without knowing.
- If a trusted certificate authority gets compromised due to security vulnerability, the application will not get affected.
Problem Associated with Certificate Pinning
A security researcher has warned the risk associated with using HTTP Certificate Pinning.
- If the key was accidentally deleted, stolen, hacked, you may face serious application downtime issues.
- Domain hijacking - on Domain-hijacking, you can lose control of certificates, and hijackers can mishandle your certificates.
After carefully evaluating, very few sites and apps use Certificate Pinning. The developer should be very careful in evaluating and using this feature. However, at this point, we have not yet implemented support for Certificate Pinning for applications build using WaveMaker.
What next?
Certificate Transparency (CT) was introduced in 2018 after deprecation of Web Certificate Pinning. CT is an open-source framework for monitoring and auditing certificates. This standard creates a public logger that records all the certificates issued by the trusted CA. You can monitor these loggers to detect mistakenly-issued certificates, compromised CAs, and CAs dishonesty.
CT in OpenSSL, whenever a connection is initiated, SSL certificates' timestamp will be used to fetch the certificate from the CT log and compared to establish the connection.
Conclusion
Though CT is different from Certificate Pinning, it will effectively replace the Certificate Pinning without compromising the quality of service.
Have a great idea for what you'd like to see next? Let us know here.