You have developed an exceptional application, and the demand for your application is increasing. You need to expand its accessibility and develop a plan to scale your application. Understanding how to scale an application means ensuring that your application can handle a larger number of users simultaneously. WaveMaker generates code based on open standards and brings best practices to the way applications should be architected. This makes scaling the application easy to understand and apply.
What happens if you don't scale your application?
It is the point when an application can no longer handle additional requests effectively that will limit its scalability. This limit is reached when the resources run out, requiring more machines or more capacity.
In this article, learn about scaling approaches and how WaveMaker scales an application.
Understanding Scaling Approaches
Following are the two approaches for scaling an application.
- Vertical Scaling
- Horizontal Scaling
Vertical Scaling
In simple terms, Vertical scaling means adding more resources to the server, for example, increasing the capacity of the CPU, RAM, and DISK space in a single machine to "scale-up". Vertical scaling is limited to the capacity of a single machine, therefore, scaling beyond that capacity often involves downtime when switching from a small machine to a bigger machine.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling means it scales an application by adding more machines into the pool across the horizontal direction to "scale-out", and the scaling is based on partitioning the data. It replicates the application by growing the number of nodes in the cluster. Also, distributing the responsibilities of each node and providing additional end-points for client connections.
Which one is better for your application?
The decision depends on a number of factors, including the following.
- Is the application request volume steadily growing?
- Is the application's current growth experiencing spikes that lead to service degradation?
Combine these factors with the application's unique requirement to evaluate and determine the optimal scaling approach.
However, when you compare both Vertical and Horizontal approaches, Horizontal scaling offers a benefit of elasticity. Instead of taking your server down while you are scaling up to a better one, you keep your existing pool of resources online while adding more to what you already have. By adding more machines to the existing pool, you are not limited to the capacity of a single machine, and that scales your application with almost no downtime, and you do not get caught into the resource-shortfall.
WaveMaker's approach for Scaling Applications
Although horizontal scaling is the desirable approach for scaling an application, there are still a few challenges that need to be addressed. Let's understand that first.
How data partition can be a challenge in Horizontal scaling
The following image shows a deployment architecture of Horizontal scaling.
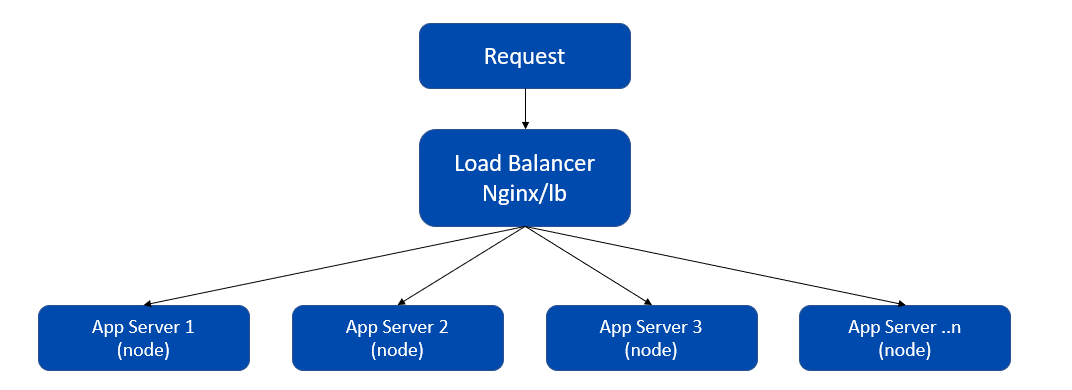
With Horizontal scaling, the data gets distributed among the nodes, and each node contains only a part of the data. Therefore, the user-session created by a node cannot be understood by the other node. In this case, when the user logins again, it rejects the request if the request goes to another node.
WaveMaker generates open standards code based on Spring for the back end. So, for Horizontal scaling, Spring Session Module implementation can be used, configured to handle session management for the application.
Integrating Spring Session with WaveMaker
Spring Session manages user's http session information while supporting clustered sessions without being tied to an application container specific solution.
In the following illustration, see how WaveMaker applications scale horizontally; specifically, storing user authenticated sessions when the requests are served by different nodes using the round-robin mechanism and without using any sticky sessions.
Distributed Persistence of User Authentication Session Architecture
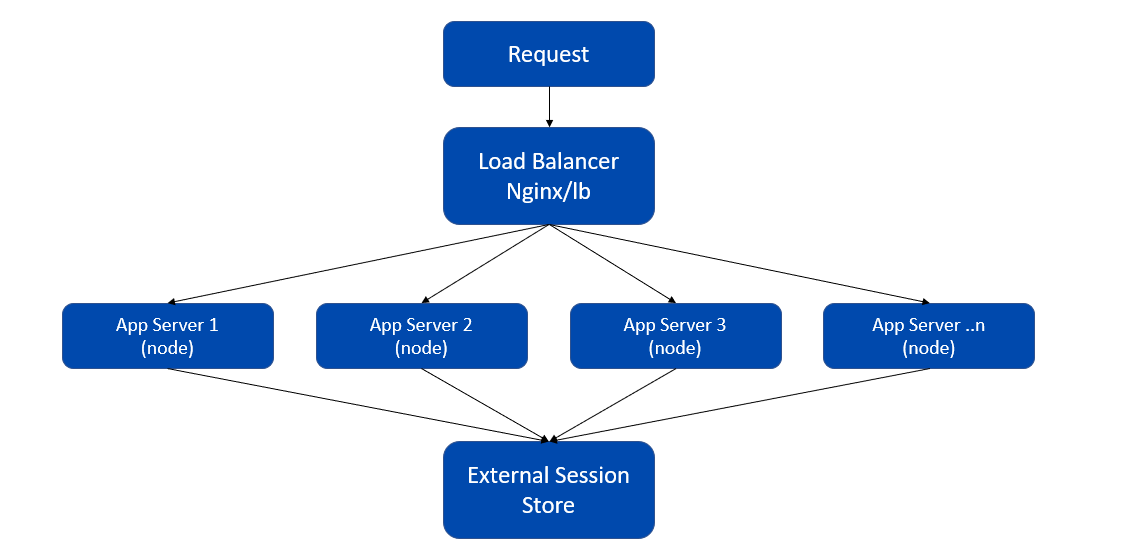
For this approach, WaveMaker uses spring-session-core as a runtime dependency. It distributes the persistence of the user authentication session. With a distributed session registry, the user session created by a node can be understood by the other nodes by persisting the user sessions in a distributed manner.
Spring-session based on External Store
There are two ways for configuring external session stores depending on your requirements by choosing from Redis and JDBC. To configure with Redis as an external store, WaveMaker adds spring-session-data-redis along with lettuce-core dependency. Similarly, for JDBC, we add a spring-session-jdbc dependency. WaveMaker internally adds these dependencies to scale applications and handle session management for the application.
With release 10.6, all the WaveMaker applications provide an option to opt for Horizontal scaling by choosing from Redis, JDBC, along with MapSessionRepository as a Distributed Session Registry.
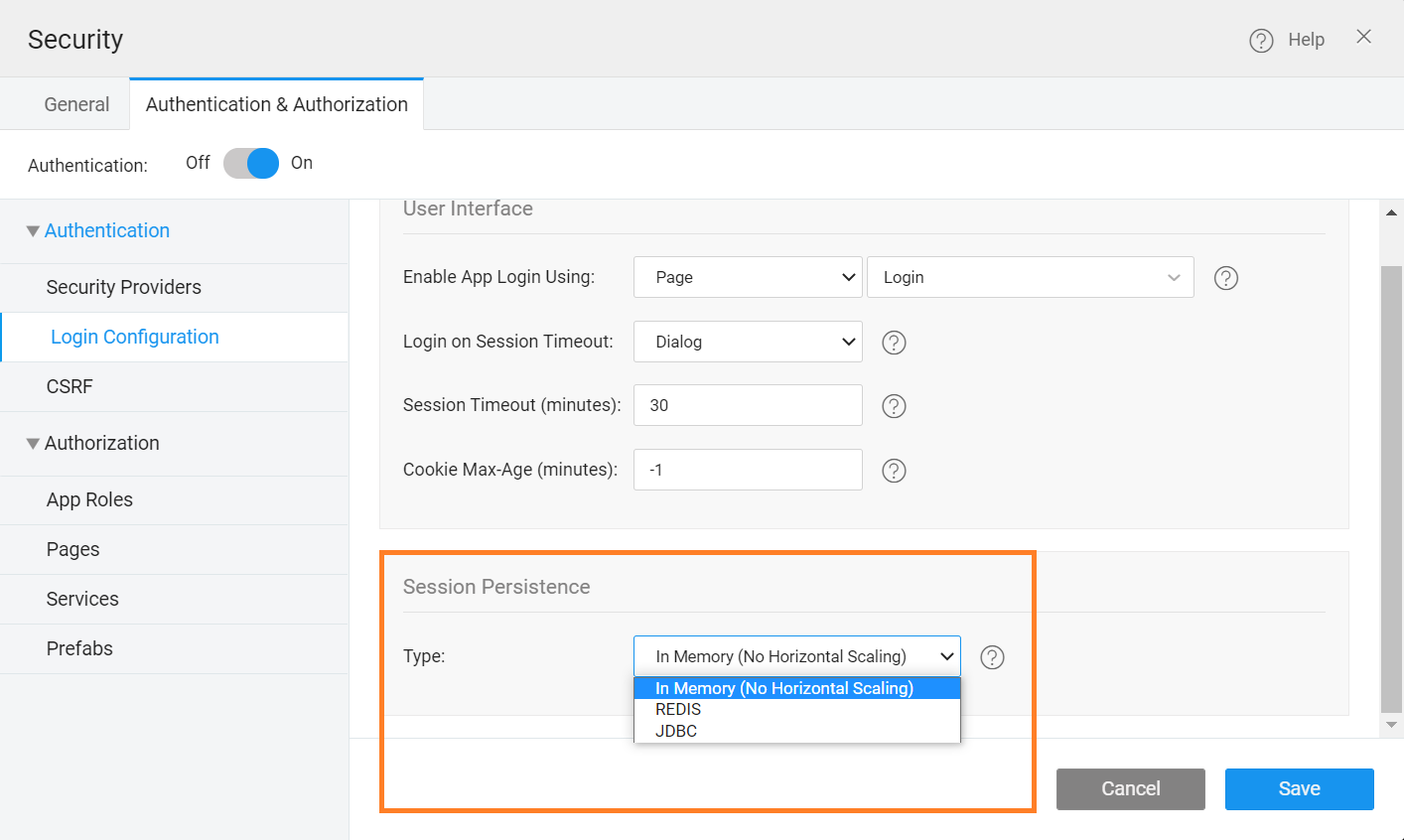
MapSessionRepository is an In-memory type that does not scale the application horizontally, and it is the default settings when you create a WaveMaker application. To enable Horizontal scaling, simply select an option from the dropdown, and follow the on-screen instructions. To learn how to use this feature, see Horizontal Scaling using Session Persistence.